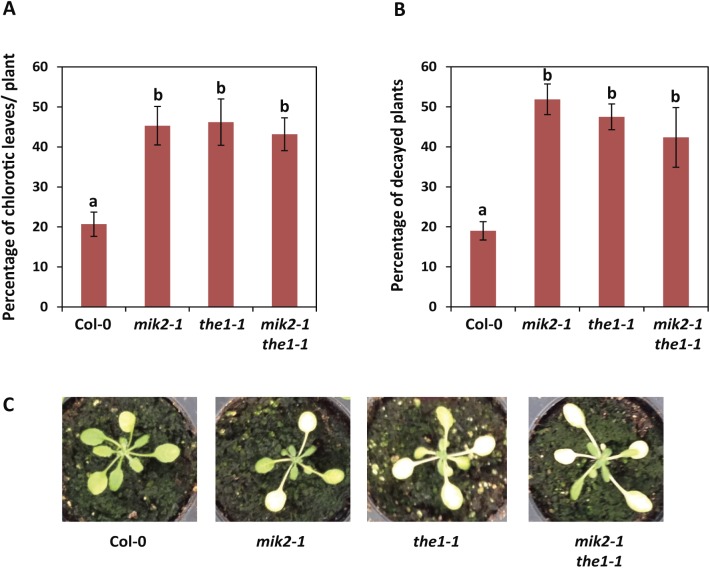
Fig 5. MIK2 is required for resistance to the fungal root pathogen Fusarium oxysporum in a THE1-independent manner.
(A,B) Percentage of chlorotic leaves per plant (A), and percentage of decayed plants (B) after infection of the roots with F. oxysporum isolate Fo5176. (A) The percentage of chlorotic leaves per plant was counted 10 days after inoculation with F. oxysporum spores. (B) The number of decayed plants was counted 3 weeks after inoculation with F. oxysporum spores. (A,B) The bars represent the average of four independent experiments, each consisting of n = 20–40 plants per genotype. Error bars represent the standard error of n = 4 experiments. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences between genotypes (ANOVA and Holm-Sidak test (p < 0.05)). No disease symptoms were observed on mock-inoculated plants for any of the genotypes (n = 10). (C) Representative pictures of the different genotypes in (A) and (B) after F. oxysporum infection.