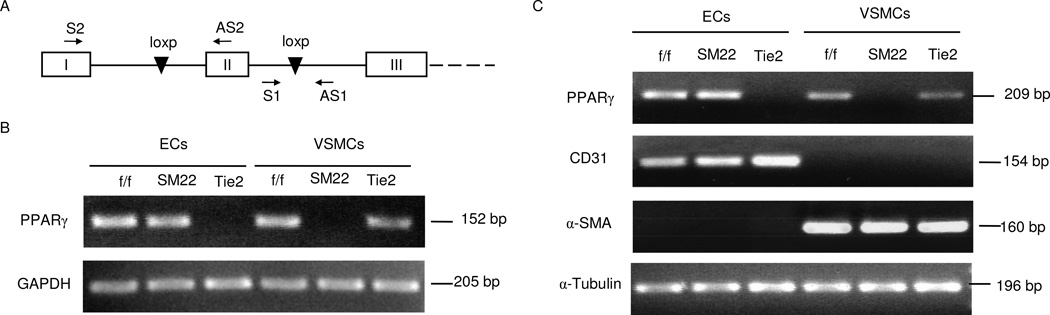
Fig. 1.
Validation of PPARγ deletion in the vascular cells. (A) Schematic illustration of primer design for detection of the PPARγ foxed allele (S1 and AS1) and PPARγ mRNA expression (S2 and AS2). (B) PCR analysis of the PPARγ floxed allele in ECs and VSMCs freshly isolated from PPARγf/f (f/f), SM22Cre/flox (SM22), Tie2Cre/flox (Tie2) mice using primers S1 and AS1. Amplification of GAPDH gene served as a loading control. C, RT-PCR analysis of PPARγ mRNA in ECs and VSMCs from the three strains of mice. CD31 and α-SMA are markers of EC and SMC, respectively. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. Shown are representatives of 2~3 experiments.