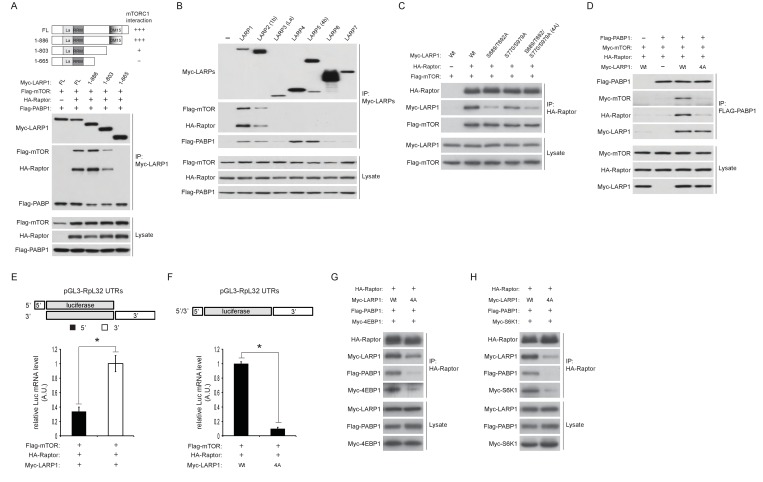
Figure 5. LARP1 scaffolds mTORC1 to LARP1-interacting mRNAs in a manner dependent on LARP1 phosphorylation.
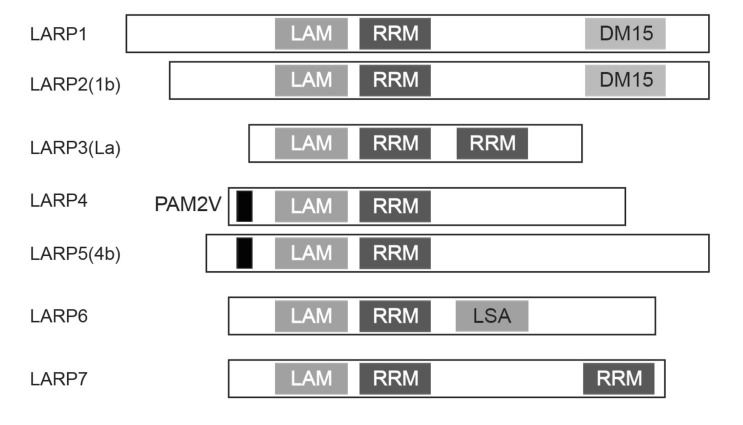
(A) The DM15 domain and its adjacent N-terminal region of LARP1 are required for the interaction with mTORC1. (B) LARP1 and LARP2 but not other LARP family members interact with mTORC1. (C) mTORC1-dependent LARP1 phosphorylation (S689/T692) plays a major role in the interaction between phosphorylated LARP1 and mTORC1. (D) mRNPs containing wild type LARP1 (Wt), but not the phospho-defective LARP1 (4A), associate with mTORC1. (E) mTORC1 preferentially interacts with the 3’UTR than the 5’UTR of RpL32 mRNA. HA-Raptor RIP assays were performed in the presence of wild type LARP1 with the indicated reporter mRNAs. Data were expressed as Figure 3A. (F) mTORC1 interacts with the RpL32 reporter mRNA in the presence of wild type but not LARP1 4A mutant. HA-Raptor RIP assays were performed. (G–H) mTORC1 more interacts with its substrates, 4EBP1 (G) and S6K1 (H) in the presence of wild type LARP1 compared to the LARP1 4A mutant.