Figure 2.
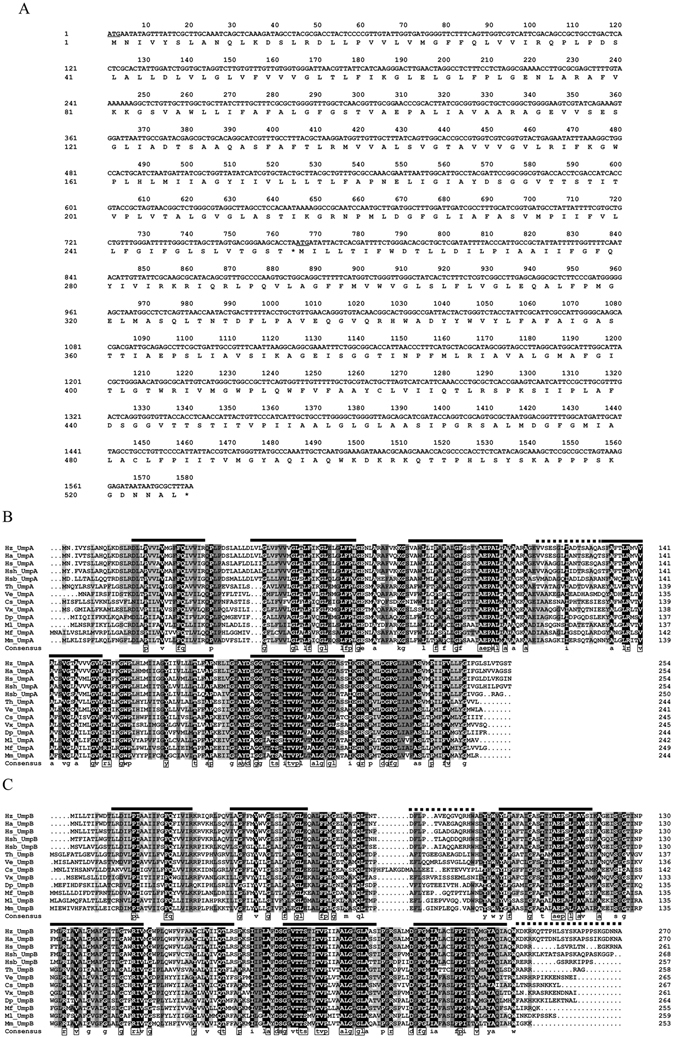
The nucleotide sequences and the deduced amino acid sequences of UmpAB and alignment of UmpAB with its most closely related holomogs clustered within the neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree. (A) The nucleotide sequences and the deduced amino acid sequences of UmpAB. Initial codons of UmpA and UmpB are underlined and stop codons are indicated by the asterisks, respectively. (B and C) Alignment between UmpAB and their respective homologs of DUF1538 family protein pairs. The 12 homologs at a range of the respective identities of 54% to 93% for UmpA and 52% to 90% for UmpB were selected, which clustered with either UmpA or UmpB within the neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree with the respective bootstrap values of 96% and 99%. Accession.version numbers and the hosts of selected UmpAB homologs are shown in the neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree in Fig. 6 and Table S1. Shading homology corresponds to 100% (black), >75% (grey), ≥50% (lightgrey) and <50% (white) amino acid identity, respectively. The seven putative transmembrane segments are marked with bold solid lines above the alignment. The additional parts of Loop III-IV for UmpA, Loop II-III for UmpB and the hydrophilic C terminus for UmpB are marked with bold dotted lines above the alignment. The highly conserved residues between UmpAB homologs are highlighted with the open rectangles in the consensus sequence.
