Figure 3.
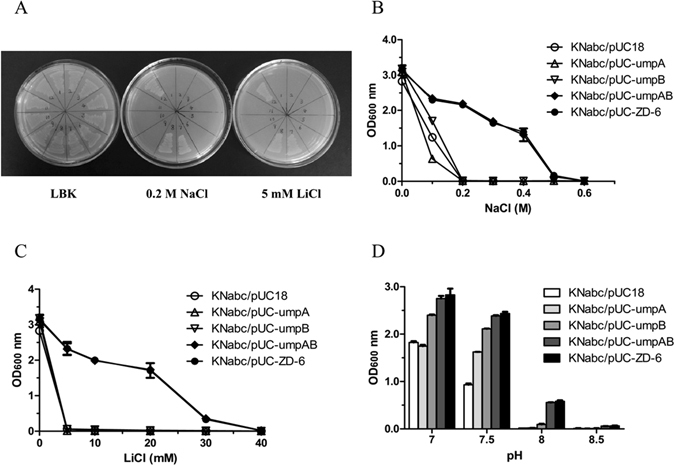
Salt tolerance and alkaline pH resistance of E. coli KNabc. For the complementation test (A), E. coli KNabc transformant cells were grown on the LBK medium plates at pH 7.0 containing no addition of NaCl or LiCl, 0.2 M NaCl or 5 mM LiCl. (1) KNabc/pET19, (2) KNabc/pET19-truncated ORF1, (3) KNabc/pUC18, (4) KNabc/pUC-ORF2, (5) KNabc/pUC-umpA, (6) KNabc/pUC-umpB, (7) KNabc/pUC-umpAB, (8) KNabc/pUC-ZD-6, (9) KNabc/pETDuet-1, (10) KNabc/pETDuet-1-umpA, (11) KNabc/pETDuet-1-umpB, (12) KNabc/pETDuet-1-umpAB. For the salt tolerance test, 1% overnight cultures of E. coli KNabc transformant cells were grown in the LBK medium at pH 7.0 containing 0–0.6 M NaCl (B), or 0–40 mM LiCl (C), followed by incubation at 37 °C. To test the effect of pH on cell growth (D), 1% overnight cultures of E. coli KNabc transformant cells were innoculated into fresh LBK medium plus 50 mM NaCl at indicated pH values (7.0–8.5) by adding the Hepes-Tris buffer (final concentration at 100 mM), followed by incubation at 37 °C. The above-mentioned cell growth was ended after 24 h and monitored turbidimetrically at 600 nm. Each data point represents the average of three independent determinations.
