Figure 2.
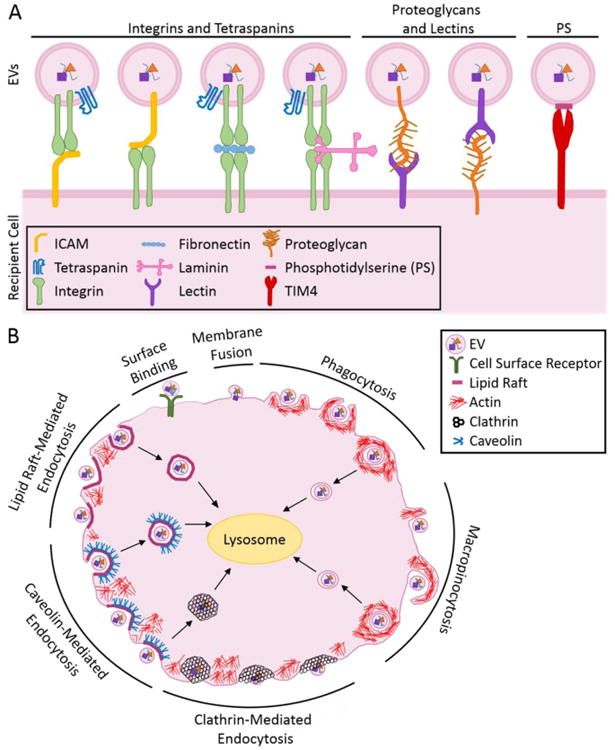
(A) EVs bind to the surfaces of recipient cells using various lipids and adhesion proteins, including tetraspanins, integrins, ECM proteins, and proteoglycans. (B) EVs interact with, and are internalized by, recipient cells via cell surface binding, membrane fusion, phagocytosis, macropinocytosis, as well as through clathrin-, caveolin-, and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis.
