Figure 2.
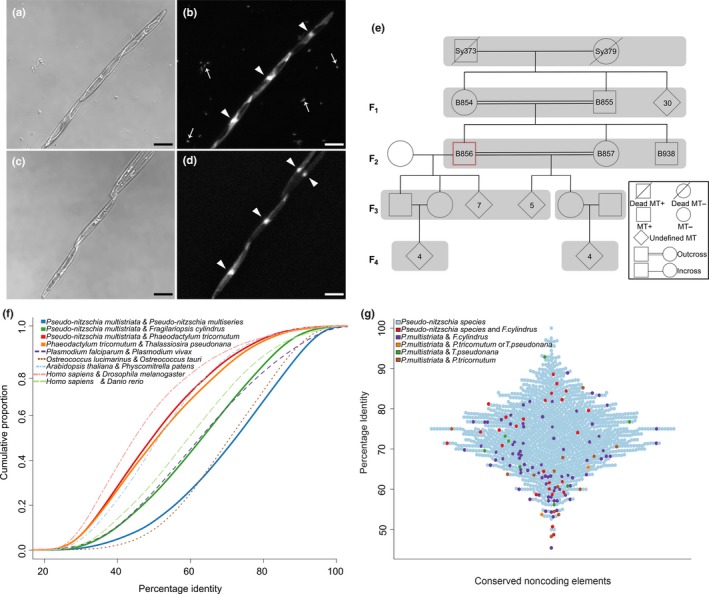
Main features of Pseudo‐nitzschia multistriata and its genome. (a, b) Microscopic images showing three cells in a chain in a normal culture with bacteria, in bright field and fluorescence, respectively, and (c, d) four cells in an axenic culture without bacteria. DAPI (4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole) stains DNA in cell nuclei (arrowheads) and bacterial nucleoids (thin arrows). Bars, 10 μm. (e) Pseudo‐nitzschia multistriata pedigree showing four generations. Strain B856 was used to produce the genome sequence. (f) Estimation of species divergence based on amino acid identity of coding genes. The x‐axis represents the average percentage identity of BLASTp hits with maximum scores for the first species against the second. The y‐axis represents the cumulative proportion of the genes showing a given percentage identity. (g) Distribution of percentage identity for noncoding elements conserved between Pseudo‐nitzschia species (light blue dots), among P. multistriata, Pseudo‐nitzschia multiseries and Fragilariopsis cylindrus (red dots) and in other combinations. The x‐axis represents the identified conserved noncoding elements, stacked for best visualization of their distribution of conservation.
