Figure 6.
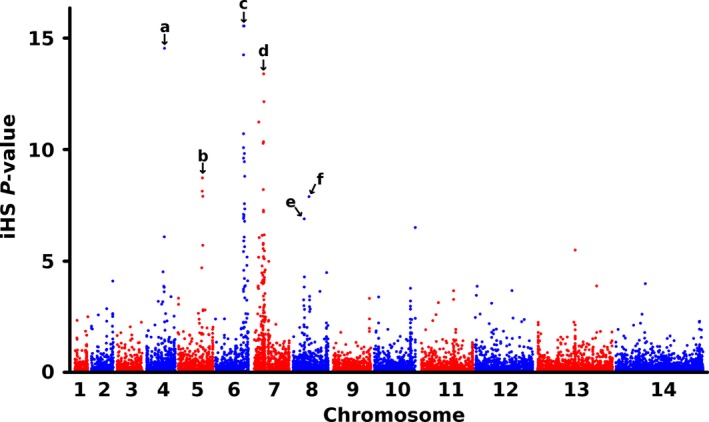
Genomewide scan for evidence of loci under positive directional selection using the standardized integrated haplotype score, plotted as ‐log10 (P‐value). Scores were calculated for 10 371 SNPs with minor allele frequency >5% using 57 unique Mauritanian clinical isolate sequences after random removal of isolates sharing >96% SNP identity with any other isolate. The scan identified 6 regions of the genome (labelled a–f) with strongest evidence of extended haplotypes: (a) chromosome (chr) 4 map region 673–765 kb covering 23 genes from PF3D7_0415200 to PF3D7_0417400, (b) chr 5 map region 908–1000 kb covering 17 genes from PF3D7_0522400 to PF3D7_0524000, (c) chr 6 map region 1087–1271 kb covering 33 genes from PF3D7_0627100 to PF3D7_0630300, (d) chr 7 map region 196–701 kb covering 119 genes from PF3D7_0704300 toPF3D7_0715900, (e) chr 8 map region 486–506 kb covering 3 genes from PF3D7_0809600 toPF3D7_0809800, (f) chr 8 map region 626–703 kb covering 21 genes from PF3D7_0812500 to PF3D7_0814500 (Table S7, Supporting information). Three of the six regions, on chr 4, 5 and 7, include antimalarial drug resistance genes dhfr, mdr1 and crt, respectively, while the two regions on chromosome 8 are positioned to either side of the drug resistance gene dhps. Only the region on chromosome 6 is not associated with a known drug resistance gene.
