Figure 1.
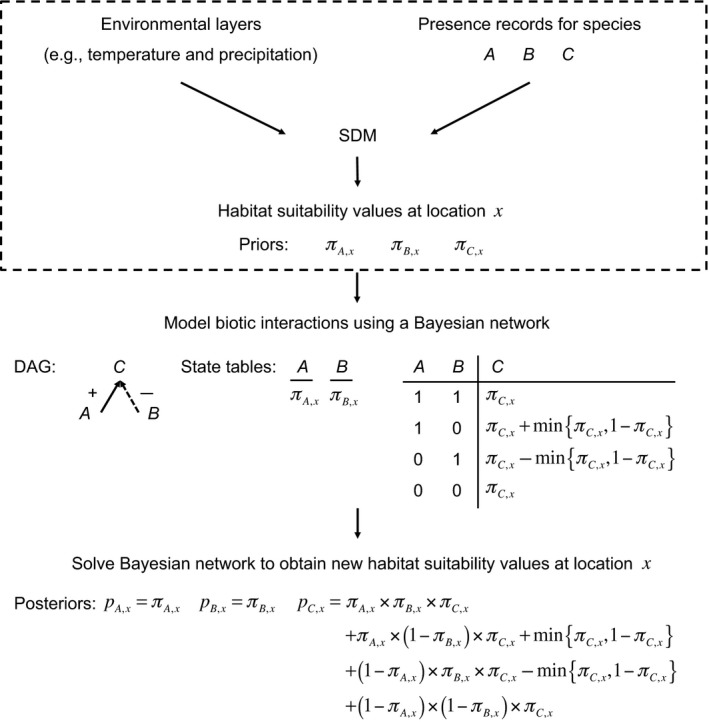
Workflow for including biotic interactions in species distribution models (SDMs): an example with three species. In a conventional SDM workflow (dashed box), data on environmental conditions and species presences are combined to predict habitat suitability across a geographical extent for species A, B and C, separately. When modelling biotic interactions using a Bayesian network (BN), we refer to the output of conventional SDMs as priors. The BN network comprises a directed acyclic graph (DAG) that describes the pattern of positive and negative conditional dependencies among species in a community, and a corresponding set of state tables that describe how each species is affected by the presence of other species (here, the presence of C is increased by the presence of A but decreased by the presence of B). The process of solving the BN transforms priors into posteriors, which now incorporate the effect of biotic interactions on habitat suitability. Note that the state table entries in this example are consistent with all three AND, OR and SUM models.
