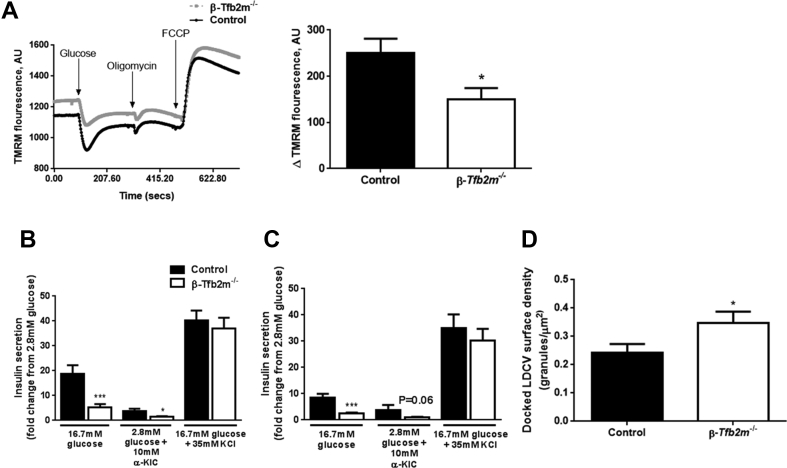
Figure 3.
Loss of Tfb2m in β-cells leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired insulin secretion. (A) Left – Kinetics of TMRM quenching in islets from control and β-Tfb2m−/− mice, n = 5 mice. Right – Change in TMRM fluorescence intensity from baseline following stimulation of isolated islets from control and β-Tfb2m−/− mice with 16.7 mM glucose, which leads to membrane hyperpolarization and minimal fluorescence intensity in quench mode, n = 5 mice. (B) Insulin secretion from islets isolated from control and β-Tfb2m−/− mice at 18 days of age. Islets were incubated for 1 h in 2.8 mM and 16.7 mM glucose, 2.8 mM glucose with 10 mM α-ketoisocaproic acid (α-KIC), and 16.7 mM glucose with 35 mM potassium chloride (KCl); control, n = 5 mice, β-Tfb2m−/−, n = 7 mice. (C) Insulin secretion from islets isolated from control and β-Tfb2m−/− mice at 35 days of age. Islets were incubated for 1 h in 2.8 mM and 16.7 mM glucose, 10 mM α-ketoisocaproic acid (α-KIC), and 16.7 mM glucose with 35 mM potassium chloride (KCl); control, n = 3 mice, β-Tfb2m−/−, n = 6 mice. (D) Surface density of docked large dense core vesicles in β-cells from control and β-Tfb2m−/− islets isolated from 18 day old mice. Granules were defined as docked if the center of the granules was within 150 nm of the plasma membrane, control and β-Tfb2m−/−, n = 4 mice each at 18 days of age. All data are mean ± s.e.m. Statistical differences were examined by unpaired Student's t-test. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 versus the corresponding value for control mice.