Table 1. Parameter estimates.
| Neutral model
|
Neutral microepidemic model
|
Epidemic clusters
|
Relative recombination rate
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | θ | ρ | θ | ρ | he | nc | 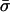 |
nrec:nmos:nmut | (r/m)pred | (r/m)obs |
| S. pneumoniae | 5.0 | 12.4 | 5.3 | 17.3 | 0.011 | 22/24 | 5.0/5.8 | 44:6:15 | 2.7 | 2.1 |
| N. meningitidis | 8.2 | 5.7 | 10.2 | 13.6 | 0.033 | 9 | 13.1 | 13:7:5 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4.6 | 0.37 | 5.6 | 0.98 | 0.026 | 7 | 13.6 | 2:0:19 | 0.13 | 0.11 |
θ and ρ are, respectively, the maximum likelihood population mutation and recombination rates obtained for the neutral multilocus model. The model fit is improved significantly by the introduction of the parameter he, which allows for an excess of identical pairs of isolates. nc and 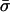 are the number and mean size of the clusters inferred from the samples (the two values for S. pneumoniae are for the Tampere, Finland, and Oxford studies, respectively). nrec, nmos and nmut are the number of pairs of isolates differing at a single locus that are classified as being the result of whole-locus recombination, mosaic recombination (i.e., recombination between a donor and recipient that occurs within the allele and produces a new mosaic allele), and point mutation by adapting the empirical method of Feil et al. (21). Patterns of descent among closely related genotypes were determined by using eburst (17) to identify ancestral and descendant alleles among strains differing at a single locus. Recombination was identified if the descendant allele was found in other lineages (eburst groups) within the sample (22). Variants differing at a single base pair were assigned as mutations; the remainder were identified as mosaic recombination. (r/m)obs is the resulting empirical estimate of the relative recombination rate, i.e., (r/m)obs = nrec/(nmos + nmut); (r/m)pred is the value predicted by our model adjusted for homozygous recombination, i.e., (r/m)pred = F′11ρ/θ.
are the number and mean size of the clusters inferred from the samples (the two values for S. pneumoniae are for the Tampere, Finland, and Oxford studies, respectively). nrec, nmos and nmut are the number of pairs of isolates differing at a single locus that are classified as being the result of whole-locus recombination, mosaic recombination (i.e., recombination between a donor and recipient that occurs within the allele and produces a new mosaic allele), and point mutation by adapting the empirical method of Feil et al. (21). Patterns of descent among closely related genotypes were determined by using eburst (17) to identify ancestral and descendant alleles among strains differing at a single locus. Recombination was identified if the descendant allele was found in other lineages (eburst groups) within the sample (22). Variants differing at a single base pair were assigned as mutations; the remainder were identified as mosaic recombination. (r/m)obs is the resulting empirical estimate of the relative recombination rate, i.e., (r/m)obs = nrec/(nmos + nmut); (r/m)pred is the value predicted by our model adjusted for homozygous recombination, i.e., (r/m)pred = F′11ρ/θ.
