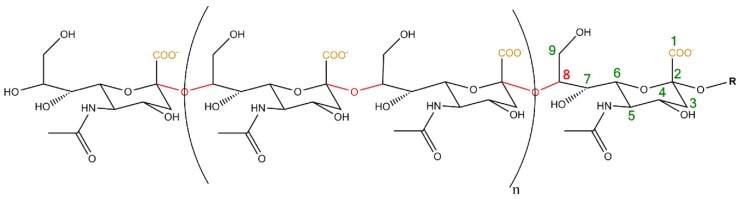
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of polysialic acid (polySia): In mammals polySia consists of α2,8-linked N-acetylneuraminic acid residues (Neu5Ac) (linkage in red). Neu5Ac belongs to the wider family of sialic acids [15,16,17]. It is an α-keto acid with a nine carbon backbone (numbering in green) bearing a carboxylate anion under physiological conditions (orange). R: N-glycan or O-glycan.