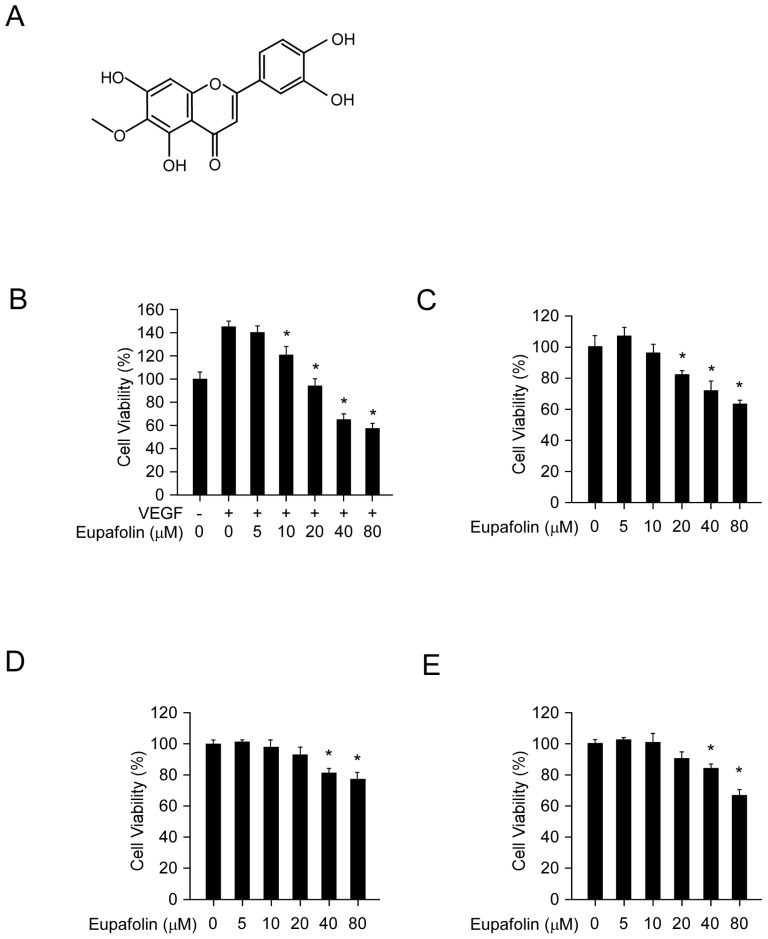
Figure 1.
Eupafolin inhibited cell viability in HUVECs and HCC cells. A, the chemical structure of eupafolin. B, eupafolin inhibited VEGF-induced HUVECs proliferation. HUVECs(2× 104/well) were seeded into 96-well plate and starved with 0.1% FBS medium overnight and then incubated with or without VEGF(20 ng/ml) and various concentrations of eupafolin for 24 h, cell viability was analyzed by MTS assay. C, inhibitory effect of eupafolin on HUVECs in normal conditions. HUVECs (2×104/well) were seeded into 96-well plate and treated with different concentrations of eupafolin for 24 h, cell viability was analyzed by MTS assay. D and E, eupafolin suppressed HCC cell lines HepG2(D) and Hep3B(E) proliferation (the conditions were the same as described in C). Columns, mean of three independent experiments ;bars, SD. The asterisk (*, p<0.05) indicated a significant decrease of cell viability after treated with eupafolin.