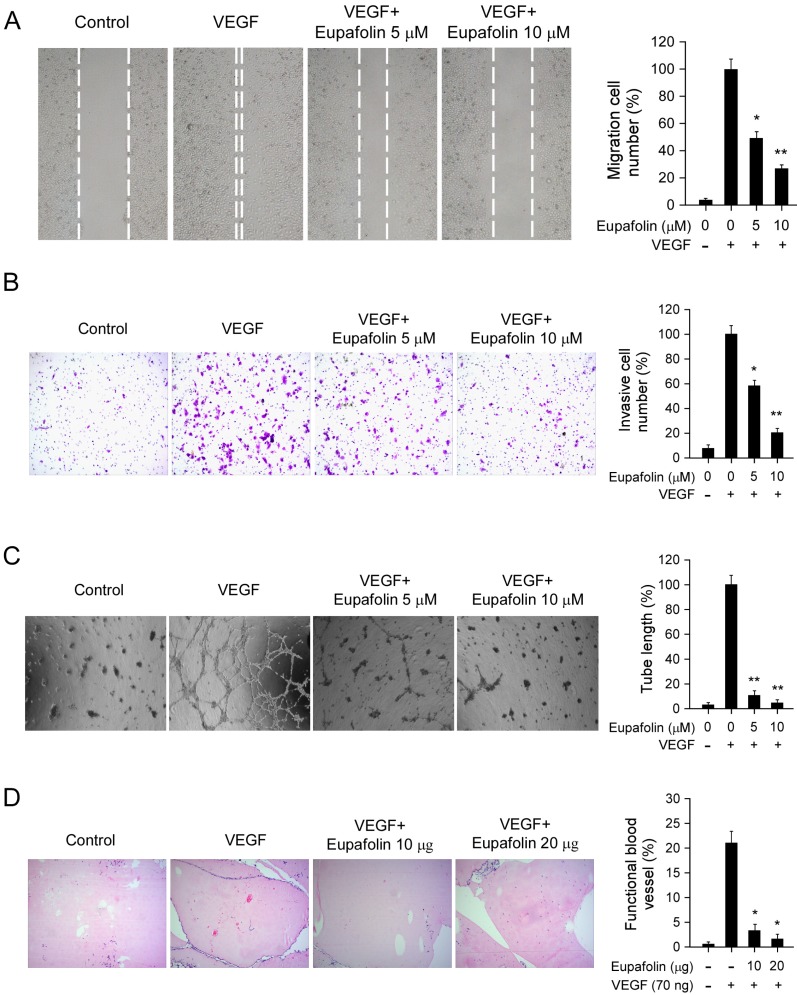
Figure 2.
Eupafolin inhibited VEGF-induced agiogenesis in vitro and ex vivo. A, eupafolin inhibited HUVECs migration. HUVECs were grown into full confluence in six-well plate and treated with 10 μg/ml mitomycin C for 2 h, then cells were wounded with pipette and incubated with or without 20 ng/ml VEGF as well as various concentrations of eupafolin. 12 h later, the migrated cells were quantified by manual counting. B, eupafolin suppressed HUVECs invasion. Cells were seeded in the upper chamber of Transwell and incubated with various concentrations of eupafolin. The bottom chamber was added with culture medium with VEGF. About 8 to 10 h later, the invasive cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet solution, the invasive cells were quantified by manual counting. C, eupafolin inhibited VEGF-induced tube formation of HUVECs. HUVECs incubated with different concentrations of eupafolin were seeded into 96-well plate pre-coated with Matrigel. After 6 to 8 h, tubular structures were photographed and the number of the tubes was quantified. D, eupafolin inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis in Matrigel plug assay. The Matrigel plug assay was performed as described in “Materials and Methods”. The number of vessels was counted. Representative photographs of each experiment (left panels) were shown, and the graph (right panels) showed the data of at least three independent experiments. Columns, mean; bars, SE; The asterisk (*, p< 0.05; **, p< 0.01) indicated significant difference versus VEGF alone.