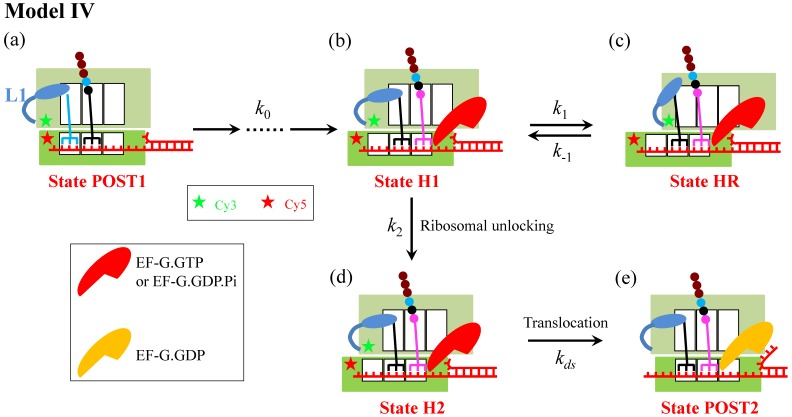
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of Model IV. From the posttranslocation state (State POST1), after rapid deacylated tRNA dissociation, the binding of the ternary complex in the A/T state, GTP hydrolysis, Pi and EF-Tu.GDP releases, the accommodation of the aminoacyl-tRNA into its fully bound A/A state and then the peptidyl transfer, the ribosomal complex transits to the classical non-rotated pretranslocation state. Then, EF-G.GTP of saturating concentration binds immediately, facilitating the classical non-rotated pretranslocation state transition to hybrid state (State H1). For convenience, the rate of transitions from State POST1 through State H1 is denoted by k0. Before the ribosomal unlocking, the transitions between rotated State H1 and hyper-rotated State HR can occur (in State HR the L1 stalk also contacts the acceptor end of the deacylated tRNA). In State H1, the ribosomal unlocking occurs (State H2). The subsequent reverse intersubunit rotation causes the small ribosomal 30S subunit translocating forward by unwinding three mRNA base pairs, with State H2 transiting to State POST2, from which the next elongation cycle continues. Schematic of the Cy3-labeled protein L9 and Cy5-labeled protein S6 in the smFRET experiments of Qin et al. 13 is shown.