Fig. 1.
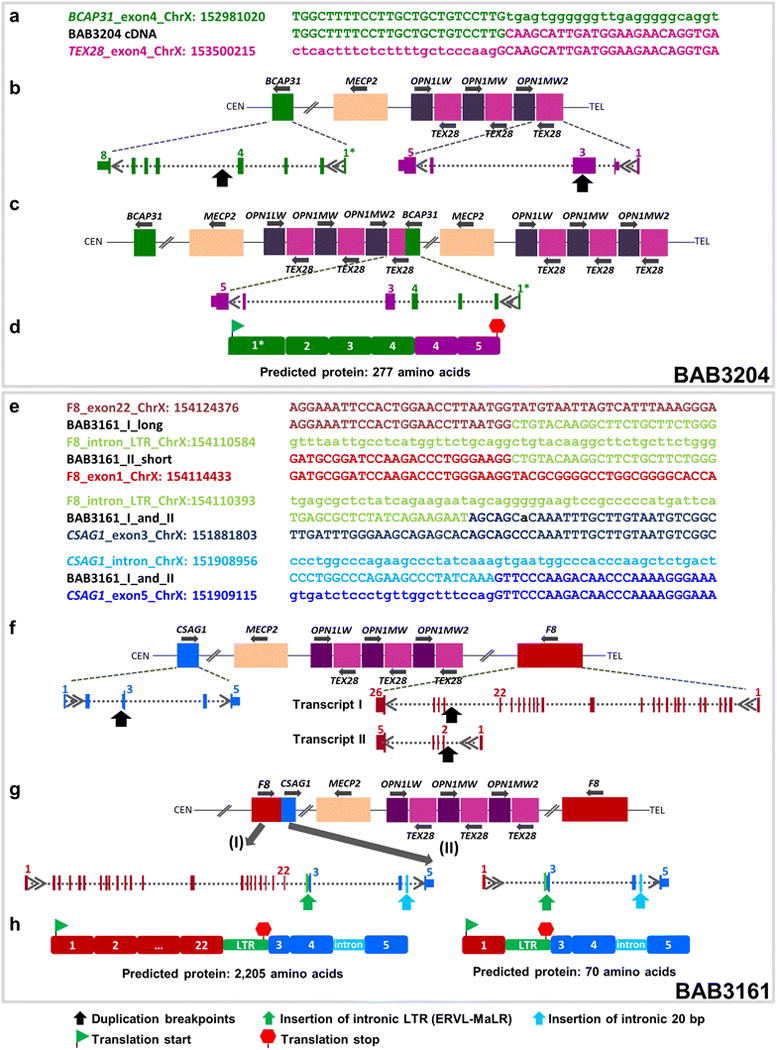
Formation of fusion genes in patients BAB3204 and BAB3161. Top Sanger sequencing of RT-PCR product using individual-specific primers targeting exons that flank genomic break-point junction. The cDNA sequences are aligned to the genomic sequences of BCAP31 and TEX28 in patient BAB3204 (a), and with the genomic sequences of F8 and CSAG1 in BAB3161 (e). For the genomic sequences, the uppercase letters represent the exons and the lowercase letters, introns. Genomic wild-type structure (b, f), post-duplication and breakpoint junction structure resulting in novel transcripts (c, g) and cDNA structures (d, h). The latter cDNA structures were obtained by RT-PCR and sequencing of the entire transcripts. In BAB3204, a duplication of ~ 462 Kb encompassing Xq28 region led to the formation of a transcribed fusion gene containing exons 1–4 from the BCAP31, plus exons 4 and 5 from TEX28 (NM_001205201.1) (c). The 1* symbol refers to the four splicing variants deposited in the RefSeq database for BCAP31 (NM_001139457.2, NM_005745.7, NM_001139441.1 and NM_001256447.1). The duplication breakpoint contains part of exon 3 of TEX28, although it is not transcribed in the cDNA. In BAB3161, a complex rearrangement constituted by two interspersed duplications of 1.45 Mb and 1.1 Mb (centromeric and telomeric, respectively) or a DUP-NML-DUP (duplication-normal-duplication) led to the formation of chimeric genes in both of the two known alternative splicing transcripts of F8, transcripts I (NM_000132.3, 26 exons) and II (NM_019863.2, five exons), fused to exons 3–5 of CSAG1 (NM_001102576.2) (g). Importantly, the genomic rearrangement generated an inversion of the F8, leading to a transcript with the same transcriptional orientation as CSAG1. Sequencing of the RT-PCR products revealed that a segment of an ERVL-MaLR repetitive element is incorporated in both transcripts. In addition, both chimeric transcripts have 20 bp from an intronic sequence between exons 4 and 5 of CSAG1 (g). The green and red flags represent computationally predicted start and termination codons in the cDNA sequences (d, h)
