Figure 4. Possible roles for TREM2 resulting from different ligands.
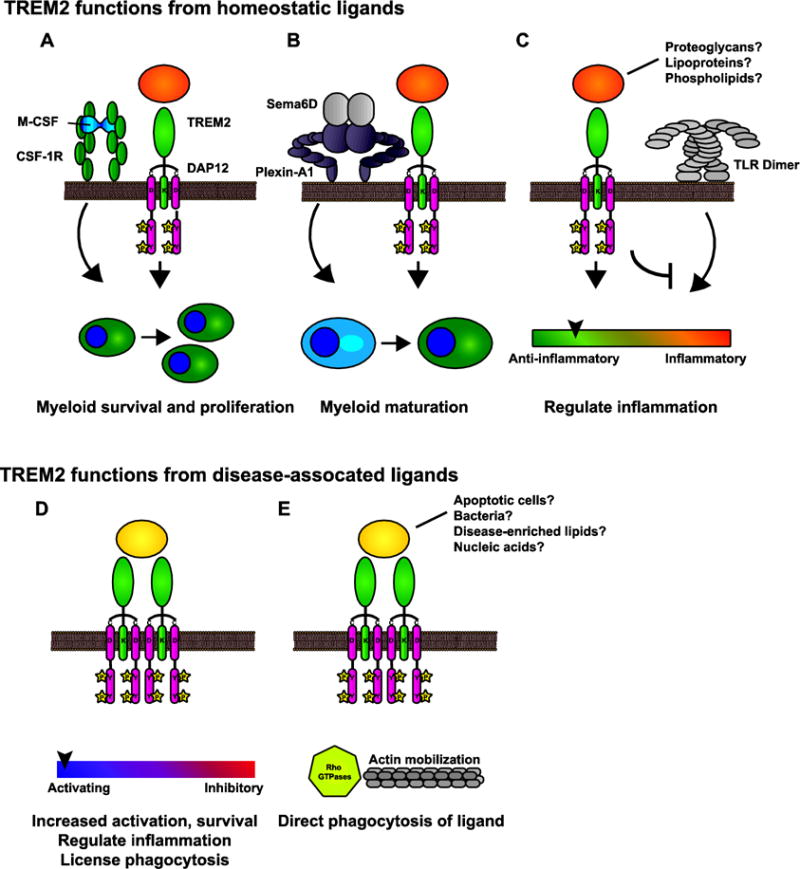
A–C) During normal conditions, TREM2 signaling from endogenous ligands permits a number of functions. A) TREM2 is a co-receptor or co-stimulatory molecule for signaling pathways such as CSF-1R involved in myeloid proliferation and survival. B) TREM2 signals (perhaps in collaboration with Plexin-A1) are important for maturation. C) TREM2 regulates inflammatory responses by influencing TLR and other activating networks to maintain homeostasis. D–E) TREM2 recognizes additional ligands associated with disease. D) These signals may increase activation and survival so that myeloid cells can respond in a context-dependent manner. E) TREM2 can induce phagocytosis of certain ligands, such as bacteria.
