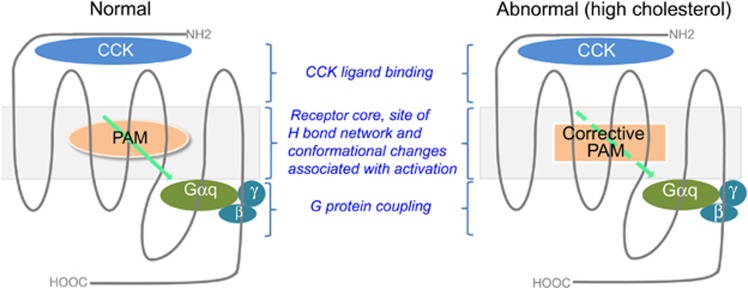
Figure 2.
Strategy for correcting abnormal stimulus–activity coupling at the CCK1R. When the CCK1R is present in a normal membrane microenvironment and functions normally, such as in normal weight people or those with a tendency to gain weight who are at the early stages of this clinical continuum, there could be clinical benefit from a PAM devoid of intrinsic activity that might augment CCK-stimulated satiety responses (left). In the later stages of this continuum when people become obese and may have metabolic syndrome, and in which CCK1R stimulus–activity coupling can be compromised because of the presence of high membrane cholesterol, a ‘corrective PAM’ might be beneficial, and perhaps even necessary, to recalibrate the function of the CCK1R (right).