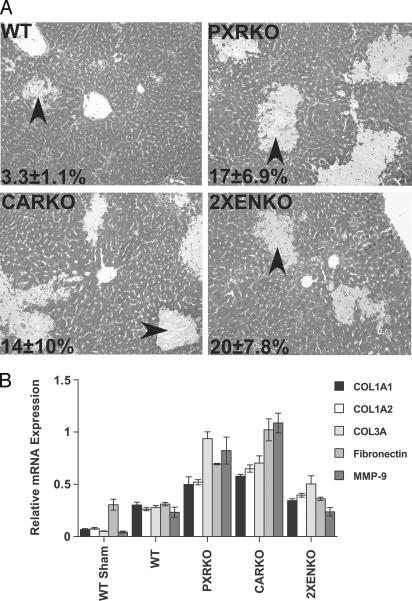
Fig. 1.
Deletion of PXR or CAR results in exacerbation of bile acid-induced liver injury. (A) Livers were removed from mice 6 days after BDL, and liver paraffin sections were stained with Gomori's Trichrome to evaluate liver injury and necrosis (n = 4–6 per group). Areas of bile infarction and hepatic necrosis (arrows) were evaluated in five microscopy fields (×10 magnification), quantified as a percentage of total area as indicated on the representative photomicrographs, and found to be increased in knockout mice relative to WT mice after BDL. PXRKO, P < 0.05; CARKO, P < 0.05; 2XENKO mice, P < 0.01. (B) Effects of BDL on hepatic expression of genes involved in fibrosis and tissue remodeling. Relative mRNA expression of collagen 1A1 (COL1A1), collagen 1A2 (COL1A2), collagen 3A (COL3A), fibronectin, and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) in liver were examined by real-time RT-PCR and normalized for U36B4 expression.