Fig. 3.
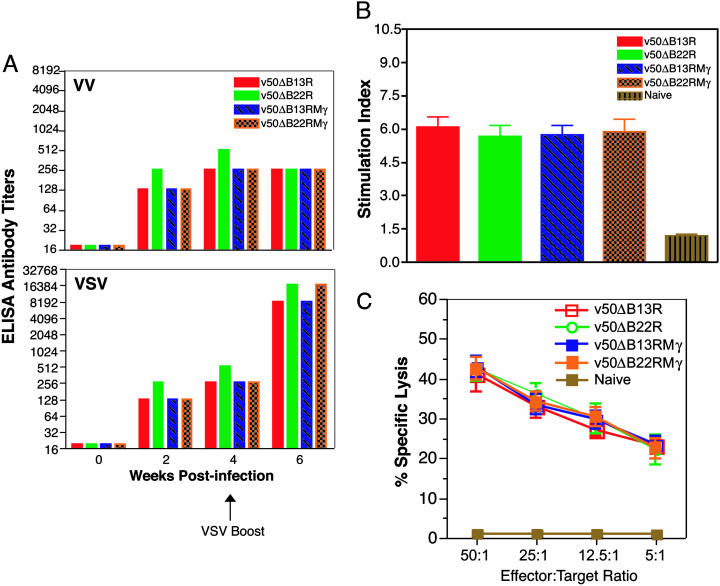
Potent immune responses are induced by rVVs expressing IFN-γ. (A) IFN-γ expression does not alter humoral responses to rVV. Antibody titers to VV (Upper) and VSV (Lower) were determined by ELISA from pooled samples assayed in duplicate. (B) rVVs coexpressing IFN-γ elicit strong T-helper responses. Splenocytes were harvested 10 days after vaccination and stimulated with 0.5 μg/ml of VSV-G. Data analysis was based on cpm in triplicates and expressed as a stimulation index. Error bars represent SD. (C) rVVs expressing IFN-γ induce potent cytotoxic T cell responses. CTL immune responses were measured 10 days after vaccination in CB6F1 mice inoculated as in B. Effector splenocytes were stimulated with haplotype matched (H-2b/d) γ-irradiated/UV-treated VSV-infected target splenocytes. Specific cytolysis values at the indicated effector/target cell ratios represent the means of triplicate experiments assayed in duplicate. Error bars represent SD.