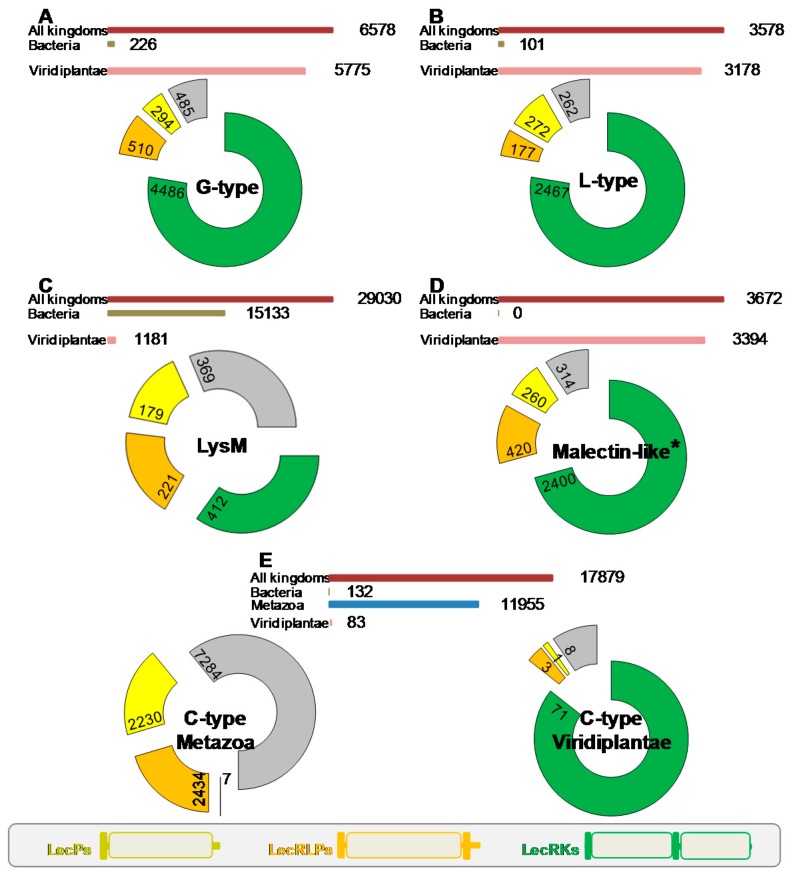
Figure 1.
Distribution of lectin domains across kingdoms and ratio of domain organizations in Viridiplantae. Data were retrieved from Pfam (pfam.xfam.org; version 31, March 2017): the number of sequences including a predicted lectin domain is indicated in Viridiplantae (pink bar), in Bacteria (brown bar), and in all kingdoms (dark pink bar). The donut charts categorized in ratio different domain organizations (see inset, bottom of the figure): a lectin domain is associated with a kinase domain (green), with a signal peptide and a trans-membrane domain (orange), with a signal peptide only (yellow), others (grey). The number of sequences in each case is indicated as well. (A) G-type lectins; (B) L-type lectins; (C) LysM domains; (D) Malectin domains. * The family considered here is Malectin_like (PF12819) that is found in a number of receptor kinases. The Malectin family (PF11721) comprised 2349 sequences with the following distribution: Viridiplantae 1493, Metazoa 227, Bacteria 314; (E) C-type lectins, distribution is shown both for Metazoa (blue bar) and Viridiplantae organisms.