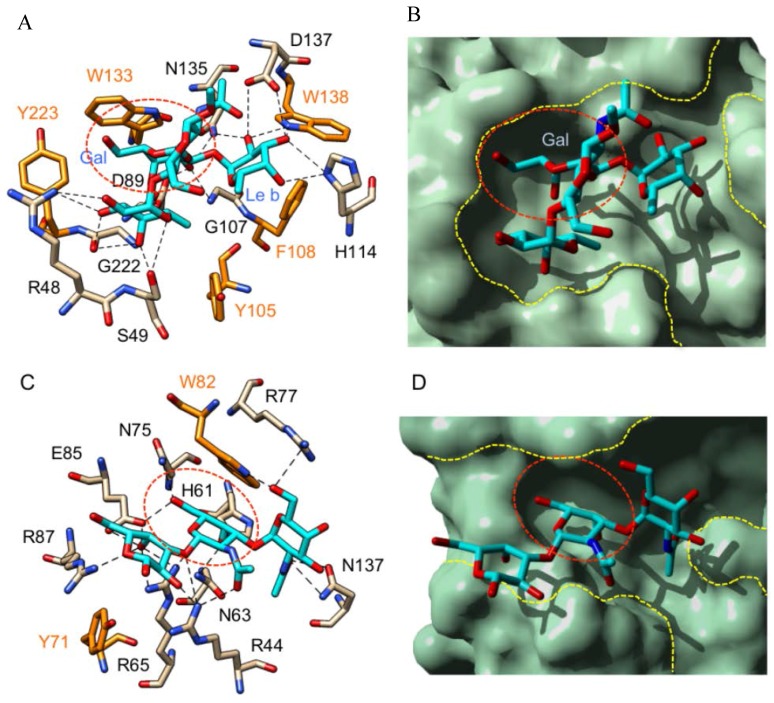
Figure 5.
(A) Network of hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) anchoring Lewis b tetrasaccharide (colored cyan) to the amino acid residues of the monosaccharide-binding site (red dashed circle) of Gs I-A4 (Griffonia simplicifolia) (PDB code 1LED) [88]. Amino acid residues involved in stacking interactions with the trisaccharide are colored orange. The Gal residue (Gal) of the Lewis b antigen occupies the monosaccharide-binding pocket of the lectin; (B) Molecular surface of Gs I-A4 showing the monosaccharide-binding site (red dashed circle) and the extended binding site (yellow dashed lines) complexed to the Lewis b trisaccharide. The Gal residue (Gal) of the Lewis b antigen occupies the monosaccharide-binding pocket of the lectin; (C) Network of hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) anchoring the Forssman trisaccharide (colored cyan) to the amino acid residues of the carbohydrate-recognition domain of galectin-9 (PDB code 2EAL) [93]. Amino acid residues involved in stacking interactions with the trisaccharide are colored orange. The red dashed circle delineates the monosaccharide-binding site of the lectin; and (D) Molecular surface of galectin-9 showing the monosaccharide-binding pocket (red dashed circle) and the extended binding site (yellow dashed lines) complexed to the Forssman trisaccharide. The penultimate GalNAc residue (GalNAc) of the Forssman antigen occupies the monosaccharide-binding pocket of the lectin. Cartoons drawn with Chimera [91].