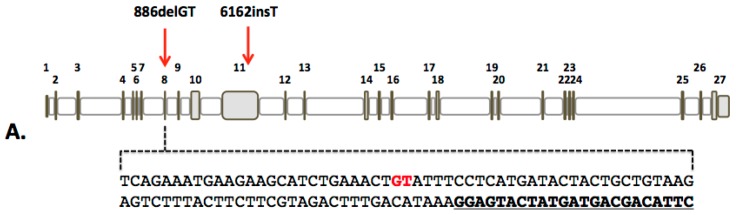
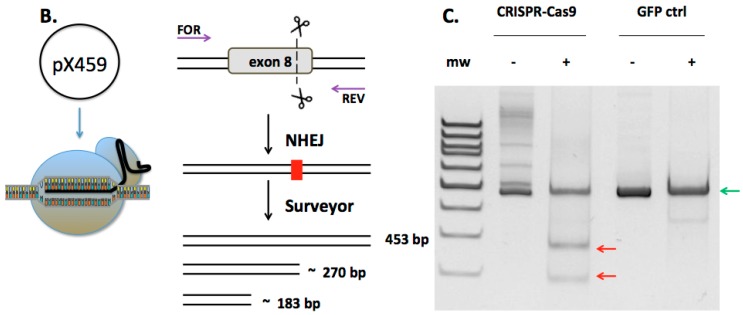
Figure 1.
FANCD1 gene and CRISPR/Cas9 reagent design. (A) FANCD1 genomic architecture with causative mutations shown with red arrows. The full exon eight sequence is shown with the bases deleted in the 886delGT mutation highlighted in red. The CRISPR/Cas9 target sequence is shown in bold and underlined; (B) CRISPR/Cas9 construct and Surveyor assay. The pX459 DNA plasmid contains both the Cas9 and the gRNA that when delivered are expressed and form the functional complex. Following plasmid delivery, a region of the FANCD1 locus was amplified using the primers indicated by purple arrows (forward (FOR) and reverse (REV)). CRISPR/Cas9 activity causes gene repair by non-homologous endjoining (NHEJ; red box). The Surveyor enzyme cleaves hybridized heteroduplexes of modified and unmodified amplicons; (C) 293 cell Surveyor analysis. The cleavage products showing FANCD1 gene modification are shown with red arrows. GFP treated controls are at right. The green arrow shows the full-length amplicon. “+” = addition of Surveyor enzyme; “−” = no Surveyor enzyme; “mw” = molecular weight standards.