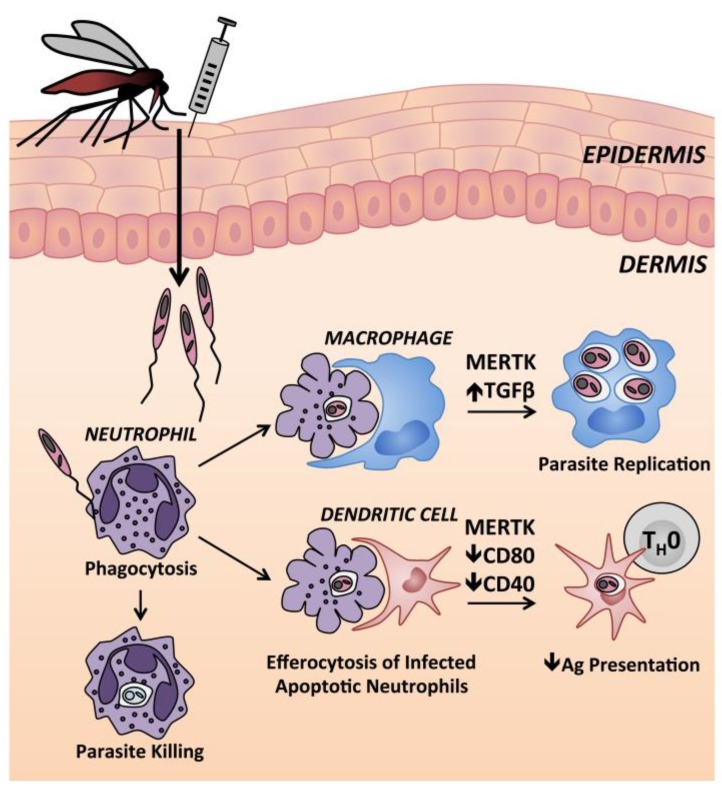
Figure 3.
Neutrophils at the cutaneous site of Leishmania spp. inoculation in mice. Neutrophils are rapidly recruited to the site of Leishmania infection, initiated by either sand fly or needle inoculation, where they phagocytose parasites. Although some Leishmania are killed by neutrophils, some survive within neutrophils until they undergo apoptosis. Uptake of apoptotic infected neutrophils by macrophages leads to MERTK signaling and increased TGFβ release, promoting an anti-inflammatory macrophage state and intracellular parasite replication. DCs that take up apoptotic infected neutrophils show a decreased capacity to present antigen to naïve CD4+ T cells. MERTK: Mer tyrosine kinase; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β, TH0: naïve CD4+ T cell.