Figure 1.
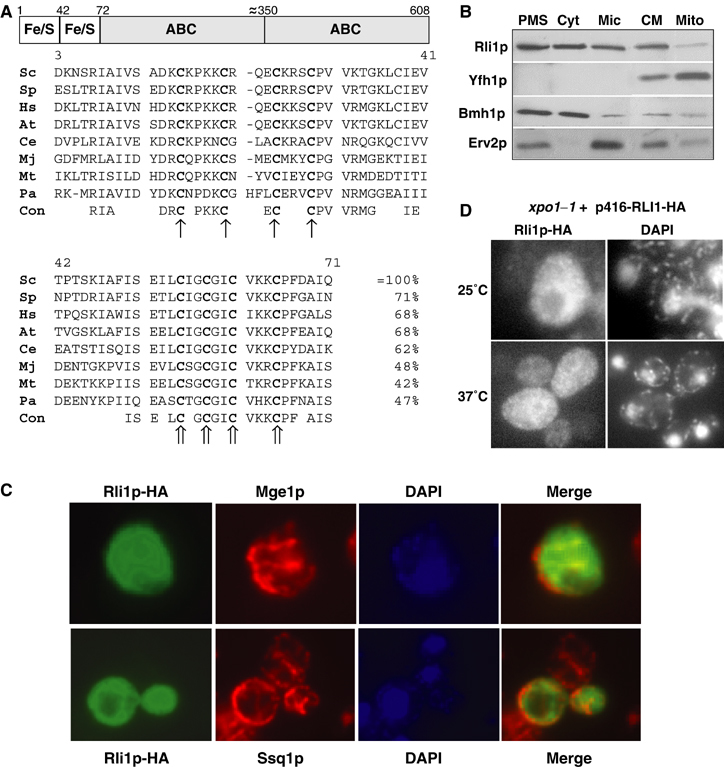
The domain structure and the subcellular localisation of Rli1p. (A) Rli1p contains two domains predicted to carry Fe/S clusters at the N-terminus and two C-terminal ABC domains. The multi-sequence alignment of the cysteine-rich regions at the N-terminus of Rli1p-like proteins was created by the Multalin program (Corpet, 1988). The conserved cysteine residues of the two ferredoxin-like motifs are labelled with different arrows. Sc, S. cerevisiae; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Hs, Homo sapiens; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Mj, Methanococcus jannaschii; Mt, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum; Pa, Pyrococcus abyssi; Con, consensus sequence. (B) Yeast cells expressing a chromosomal version of Rli1p-HA were subfractionated by differential centrifugation. A post-mitochondrial supernatant (PMS) and a crude mitochondrial (CM) fraction were obtained by centrifugation of the cell lysate for 10 min at 10 000 r.p.m. The PMS fraction was used to separate soluble cytosolic proteins (Cyt) from a microsomal membrane fraction (Mic) by centrifugation at 100 000 r.p.m. for 1 h. Mitochondria (Mito) were purified from the CM fraction by Nycodenz density gradient centrifugation. Equal amounts of protein were analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunostaining for Rli1-HA and the indicated marker proteins (Yfh1p, mitochondrial matrix; Bmh1p, cytosol; Erv2p, endoplasmic reticulum). (C) In situ immunofluorescence labelling of Rli1p-HA and mitochondrial proteins Mge1p and Ssq1p. Wild-type cells (strain PSY581) were transformed with the high-copy expression vector p426 containing RLI1-HA, labelled with antibodies against the HA-tag, Ssq1p or Mge1p, and stained with fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies. DNA was counterstained with the fluorescent dye DAPI. Merged images show no co-localisation of Rli1p-HA with Mge1p or Ssq1p. (D) A fraction of Rli1p shuttles between cytosol and nucleus. xpo1–1 cells expressing Rli1p-HA (plasmid p416) were grown in minimal medium at 25°C to OD600 of 0.4. Cells were shifted to 37°C for 15 min and examined by fluorescence microscopy.
