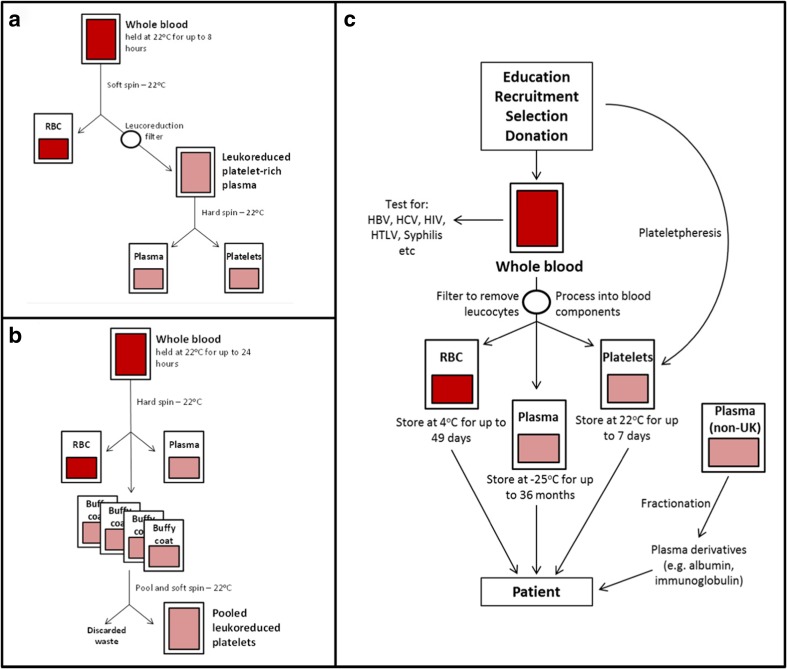
Fig. 2.
Schematic depicting methods for the separation and storage of blood-derived cellular products and plasma. a Platelet-rich plasma is produced by separation of RBC followed by leukoreduction. b Buffy coat is obtained after separation of plasma and the platelet and leukocyte enriched cell fraction from RBC either from one individual or from pooling several donations followed by leukoreduction to get PC. c General overview of blood processing after donor selection and testing. RBC is always provided by individual donation, while a pool of 4–6 blood donations or plasmapheresis is used for preparation of PC. Between 1000 and >10,000 plasma donations are pooled for protein preparation as FVIII and FIX [24, 25]. Non-UK plasma is used in all countries to avoid the risk of prion contamination; in the UK, non-UK plasma is used for patients born after 1 January 1996 [24]. HBV hepatitis B virus, HCV hepatitis C virus, HIV human immunodeficiency virus, HTLV-1 human T-lymphotropic virus type 1. This figure was adapted from the Handbook for Transfusion Medicine, 5th Edition [24] and Vassallo and Murphy 2006 [25]