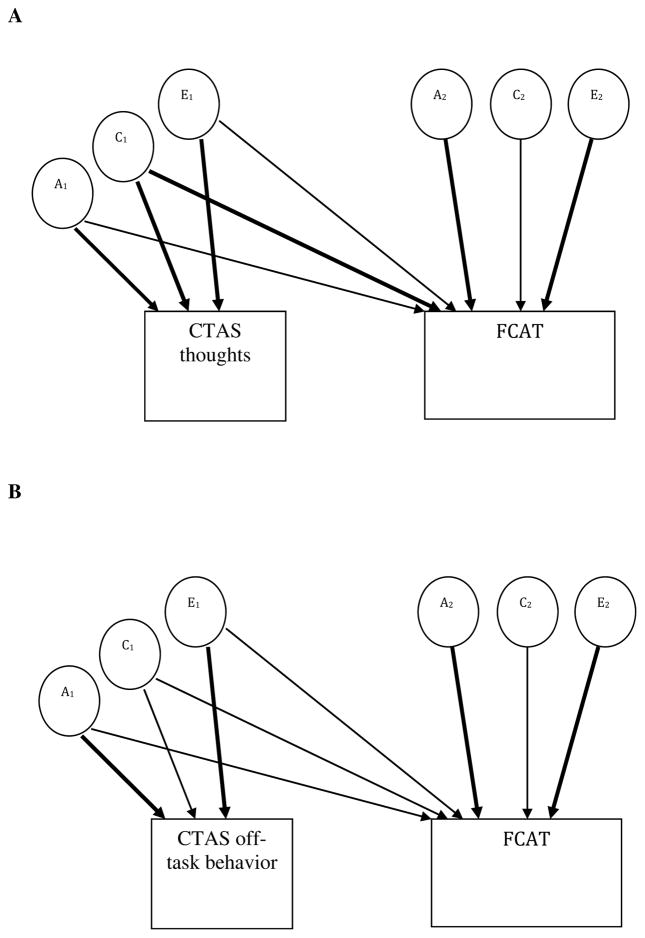
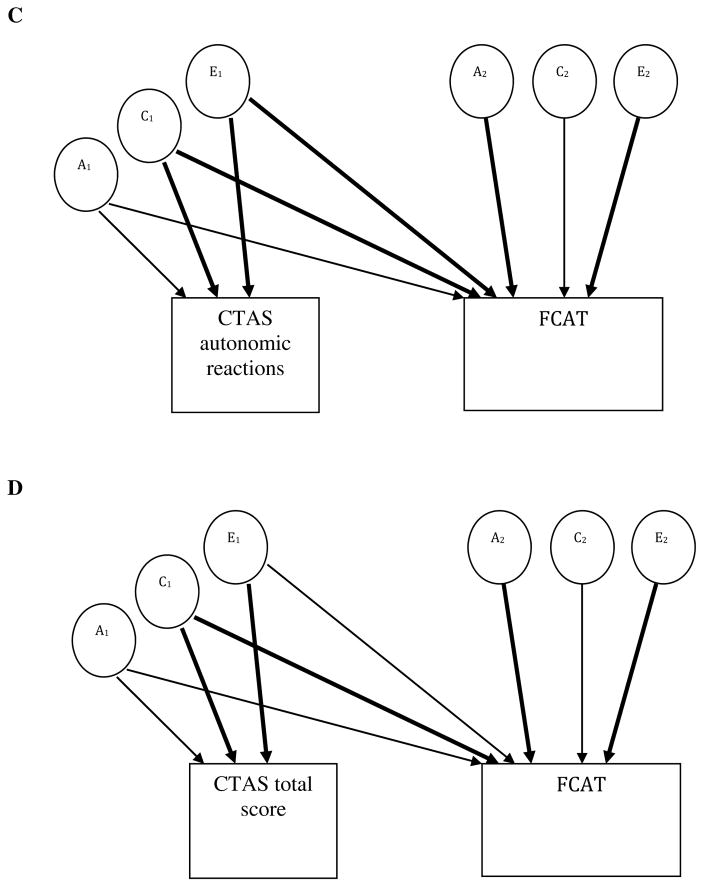
Figure 1.
Bivariate Cholesky modeling of test anxiety and the Florida Comprehensive Achievement Test (FCAT). Each of the three bivariate Cholesky models (panels A–C) contained a test anxiety dimension (thoughts, off-task behavior, and autonomic reactions, respectively) and FCAT. Additionally, a fourth bivariate Cholesky model for the full test anxiety measure and reading comprehension was included (panel D). In the model, variance and covariance were decomposed into additive genetic (A), shared environmental (C), and nonshared environmental (E) factors. Significant pathways are noted by bold arrows. CTAS, Children’s Test Anxiety Scale.