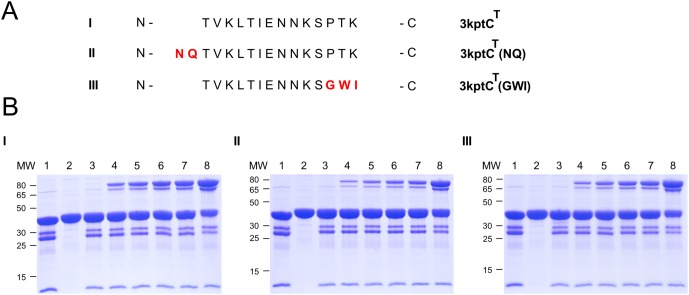
Fig 11. Comparative analysis of different 3kptCT-MBP variants.
(A) Sequence alignment of different 3kptCT-MBP variants (I: 3kptCT wildtype (residues T505-K518), II: N-terminal N506-Q507 extension of 3kptCT, III: C-terminal GWI instead of PTK in 3kptCT). (B) Comparative covalent intermolecular bond formation assay between different 3kptCT-MBP variants and mCherry-3kptCC. Purified 3kptCT variants and mCherry-3kptCC proteins were mixed each at 15 μM (final conc.) for 24h at 25°C with shaking at 500 rpm before boiling (10min, 95°C) and SDS-PAGE with Coomassie staining. Interaction I: mCherry-3kptCC + 3kptCT (wildtype), interaction II: mCherry-3kptCC + 3kptCT (NQ), interaction III: mCherry-3kptCC + 3kptCT (GWI). (lane 1: mCherry-catcher input (30μM), lane 2: tag input (30μM), lane 3: 0h, lane 4: 1h, lane 5: 2h, lane 6: 3h, lane 7: 4h, lane 8: 24h). Same volume of samples were loaded. MW stands for molecular weight (kDa).