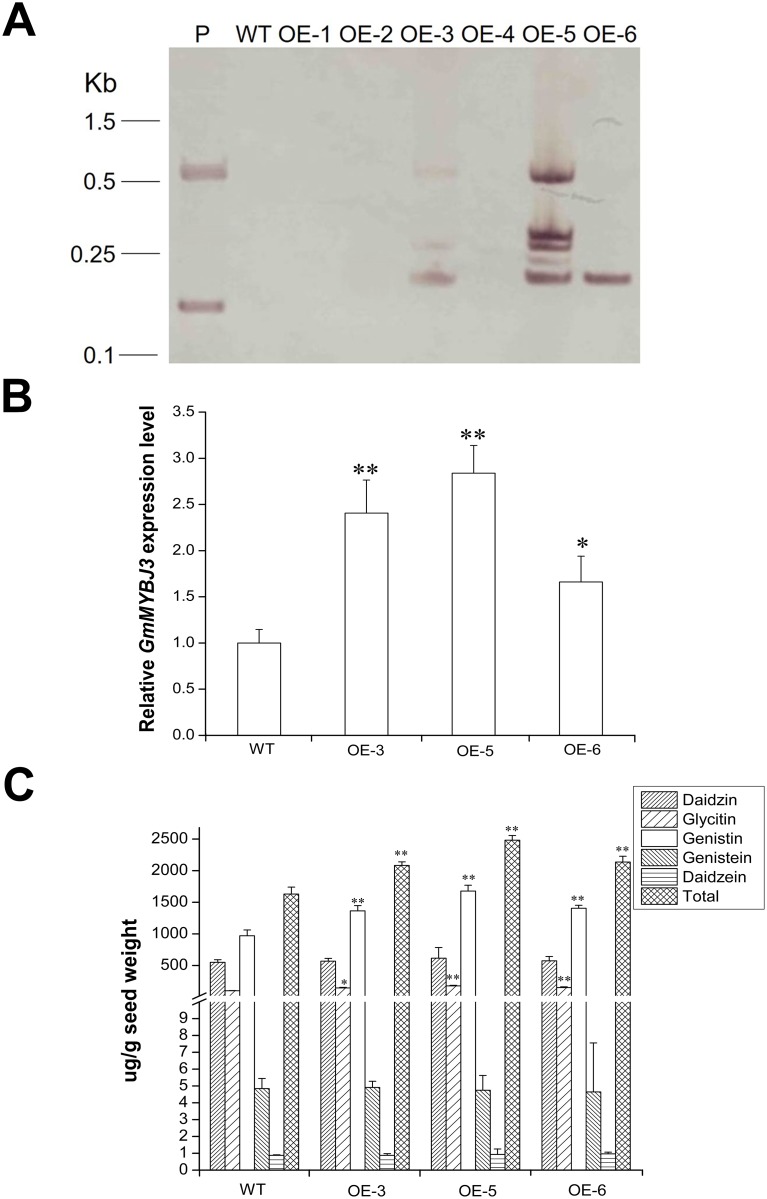
Fig 7. Genetic transformation and analysis of GmMYBJ3 in soybean.
(A) Southern blot analysis of T2 transgenic plants using the bar gene fragment as a probe. The DNAs of transgenic plants were digested with Hind III. The bands present in the transgenic lines, but undetected in the wild type were used to define the positive transgenic plants. P, pCB35SR1R2-GFP-GmMYBJ3 vector DNA used as a positive control; WT, wild type; OE, GmMYBJ3 overexpression lines, with 1–6 representing different transgenic lines. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showing the expression level of GmMYBJ3 in the seeds of the positive T2 transgenic plants compared to the wild type, Jilin 35 (control). Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent seeds, with each plant having three technical replicates. * and ** represent significant differences at P ≤ 0.05 and 0.01 between the transgenic lines and the WT. (C) Isoflavonoid content in the seeds of the positive T2 transgenic compared to the WT control. The data of wild type (control) represent the mean ± SD of three independent plants, with each plant having three technical replicates. The data for each of the independent positive transgenic lines are the means of three technical replicates, and the error bars show SEM. * and ** represent significant difference at P ≤ 0.05 and 0.01 between the transgenic lines and the WT.