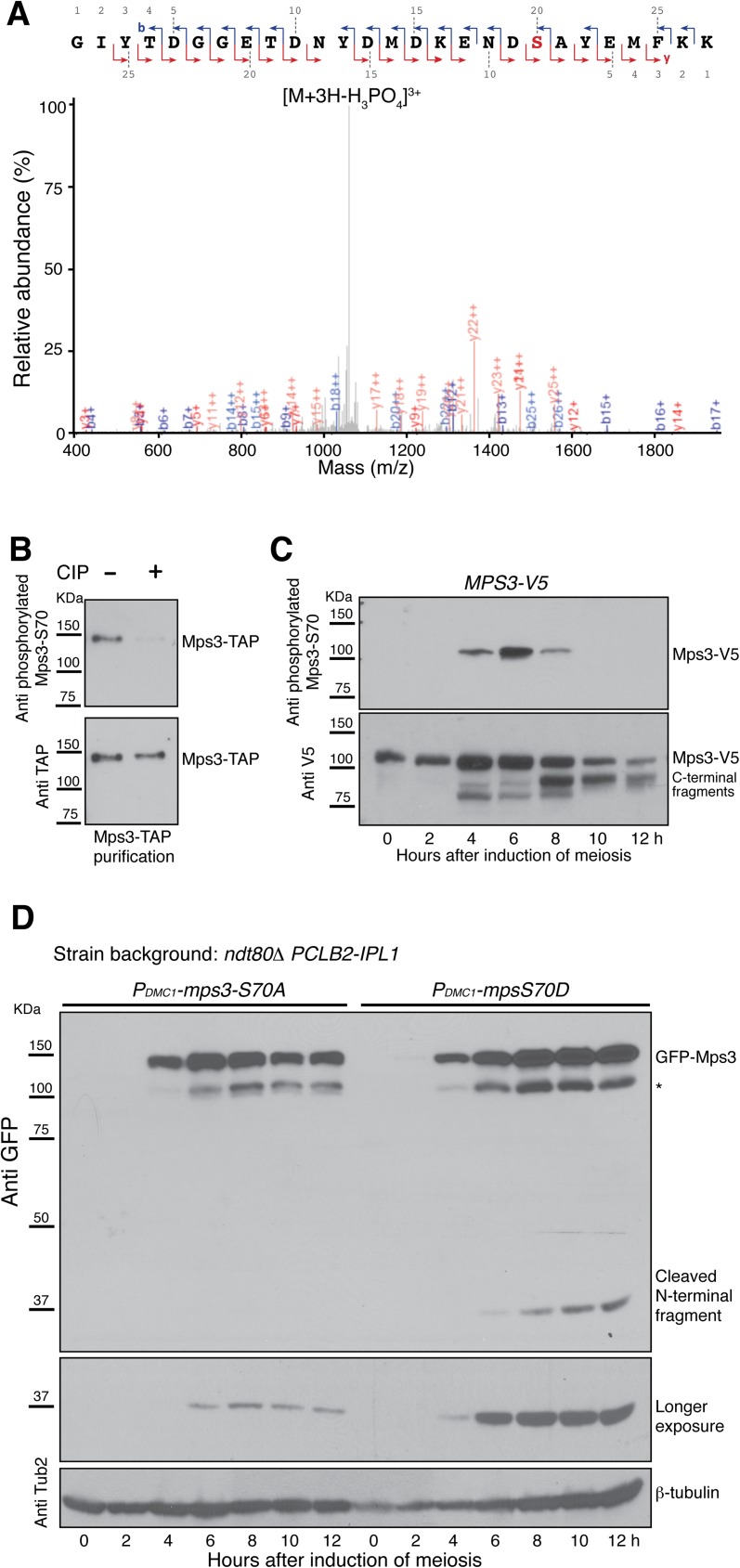
Fig 4. Phosphorylation at serine 70 promotes Mps3 cleavage.
(A) Mass-spectrometry analysis of Mps3 phosphorylation. Yeast SPBs were affinity purified with Spc97-TAP, phosphopeptides were enriched and subjected to mass spectrometry. Mass to charge ratio (m/z) is shown at the x axis. The fragmentation map is shown at the top. Singly charged b-ions are shown in blue, y-ions in red, and doubly and triply charged ions in grey. Strain HY3674. (B) Mps3 is phosphorylated at S70 during yeast meiosis. Mps3-TAP was affinity purified from meiotic yeast cells and treated with the alkaline phosphatase (CIP). A phosphospecific antibody was used to determine phosphorylation at S70 of Mps3. Strain HY3810. (C) The timing of Mps3-S70 phosphorylation during meiosis. Yeast cells were induced to undergo synchronous meiosis, and protein extracts were prepared for western blotting. Note that Mps3 is highly phosphorylated at S70 6 h after the induction of meiosis. Strain HY5568. (D) Effect of Mps3 phosphorylation on Mps3 cleavage. Yeast cells were induced to undergo synchronous meiosis, and western blots were performed to probe the presence of the N-terminal fragment resulted from Mps3 cleavage. Note that Mps3-S70A, but not Mps3-S70D, inhibited Mps3 cleavage. * Degradation product of GFP-Mps3. Strains HY4431 and HY4468.