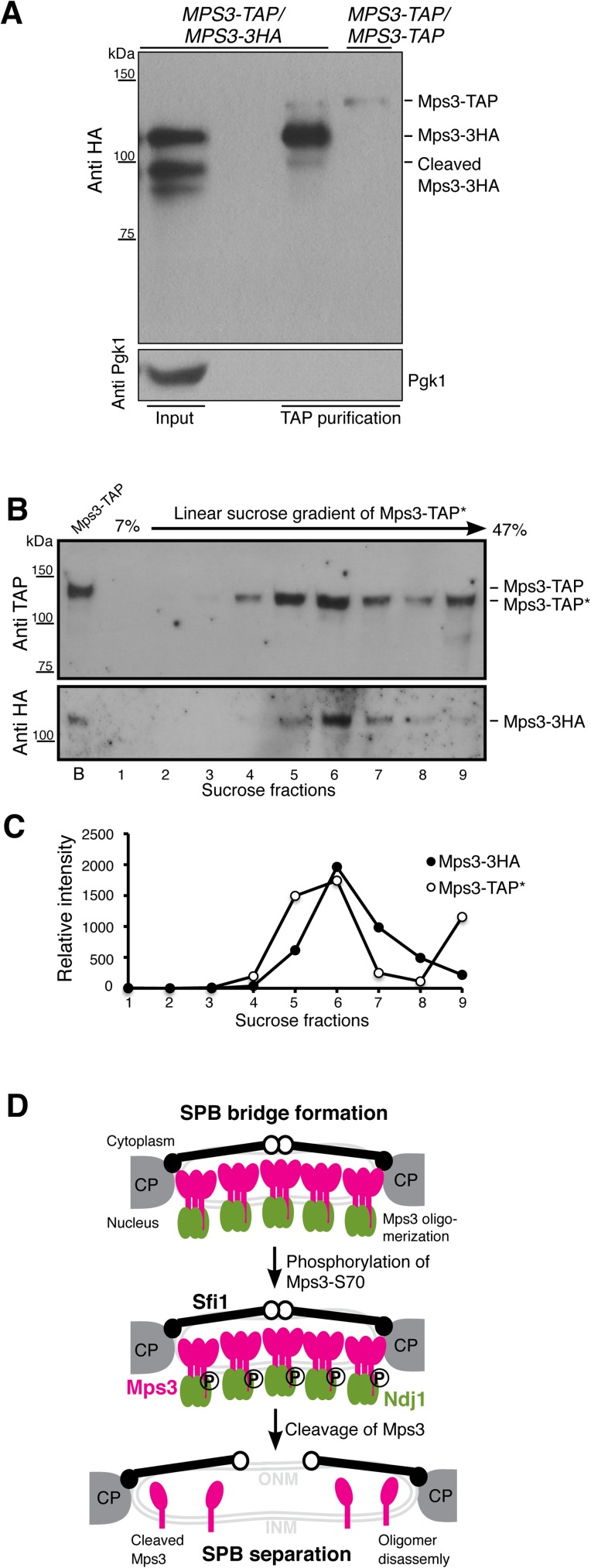
Fig 8. Model for Mps3 action during SPB separation.
(A) Affinity protein purification showing that Mps3 forms protein oligomers during yeast meiosis. In the diploid yeast cell (HY4394), one copy of MPS3 was tagged with TAP, the homologous copy was tagged with 3xHA, both to the C-terminus of Mps3. Yeast cells were induced to undergo synchronous meiosis for 5 h, and 2 liters of cells were harvested for protein affinity purification, followed by western blotting. Note that the full-length Mps3 minimally interacts with its cleaved form. Because the secondary antibody also recognizes the protein A peptide domain of the Mps3-TAP, here the MPS3-TAP/MPS3-TAP strain (HY3810) serves as a control to show the position of Mps3-TAP on the western blot. (B and C) TEV-cleaved Mps3-TAP* and Mps3-3HA peaked in the same sucrose fraction. Mps3-TAP was affinity purified as in A, followed by TEV protease treatment to remove the protein A peptide domain, thus releasing Mps3-TAP* from the magnetic beads. Affinity purified protein complexes were then fractionated by centrifugation in a linear sucrose gradient. Western blotting was used to determine the presence of Mps3-TAP* and Mps3-3HA in sucrose fractions. TAP* denotes the removal of the protein A domain from the TAP tag, thus Mps3-TAP* by itself can no longer be recognized by the secondary antibody. Lane B denotes bead-bound Mps3-TAP before TEV treatment, which has a higher molecular weight than TEV-cleaved Mps3-TAP*. Quantification of signal intensity of Mps3-TAP* and Mps3-3HA was shown in C. (D) Model for Mps3 cleavage and SPB separation. Mps3 is shown as red lollipops, Ndj1 as green ovals, and Sfi1 as black lines with a closed (N-terminus) and an open (C-terminus) dot. Part of the central plaque (CP) is shown in the diagrams of the SPB half-bridge.