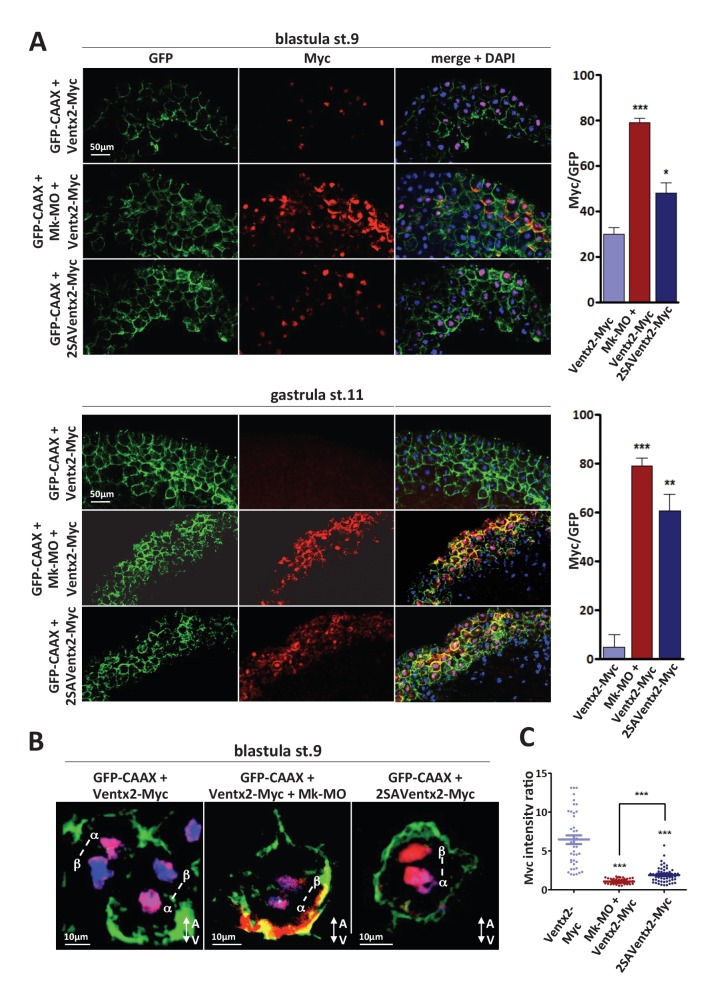
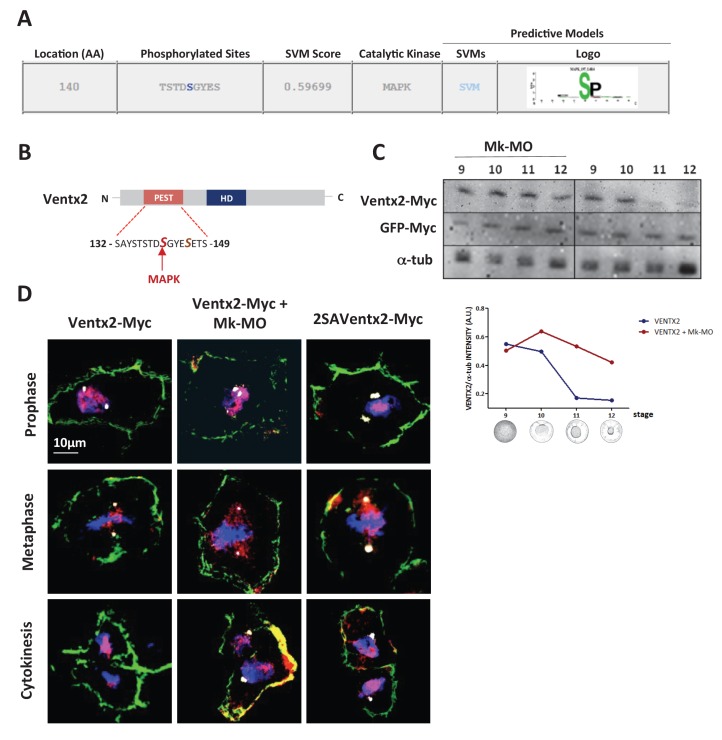
Figure 3. MEK1 is required for Ventx2 clearance and asymmetric distribution during cell division.
(A,B) Four-cell embryos were injected in each cell with 50 pg GFP-CAAX, 50 pg Ventx2-Myc, 50 pg 2SAVentx2-Myc RNAs, and 25 ng Mk-MO, as indicated. Embryos were fixed at blastula stage 9, or gastrula stage 11, cryosectioned and processed for anti-Myc (red), and anti-GFP (green) immunostaining, and DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Graphs show the percentage of Myc positive nuclei (DAPI positive) over the total number of injected cells (GFP positive) from four independent experiments. (B) 3D reconstruction of confocal slices of mitotic Myc positive nuclei labeled by DAPI from stage nine sectioned embryos. Sister mitotic chromosomes are referred to as α (more intense Myc staining), and β (less intense Myc staining). The A-V arrows indicate the animal-vegetal axis. Note the asymmetric cortical Ventx2-Myc signal in the MEK1 morphant cell. (C). The graph shows the ratios of Myc signal intensity betweenα and β sister nuclei.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21526.009