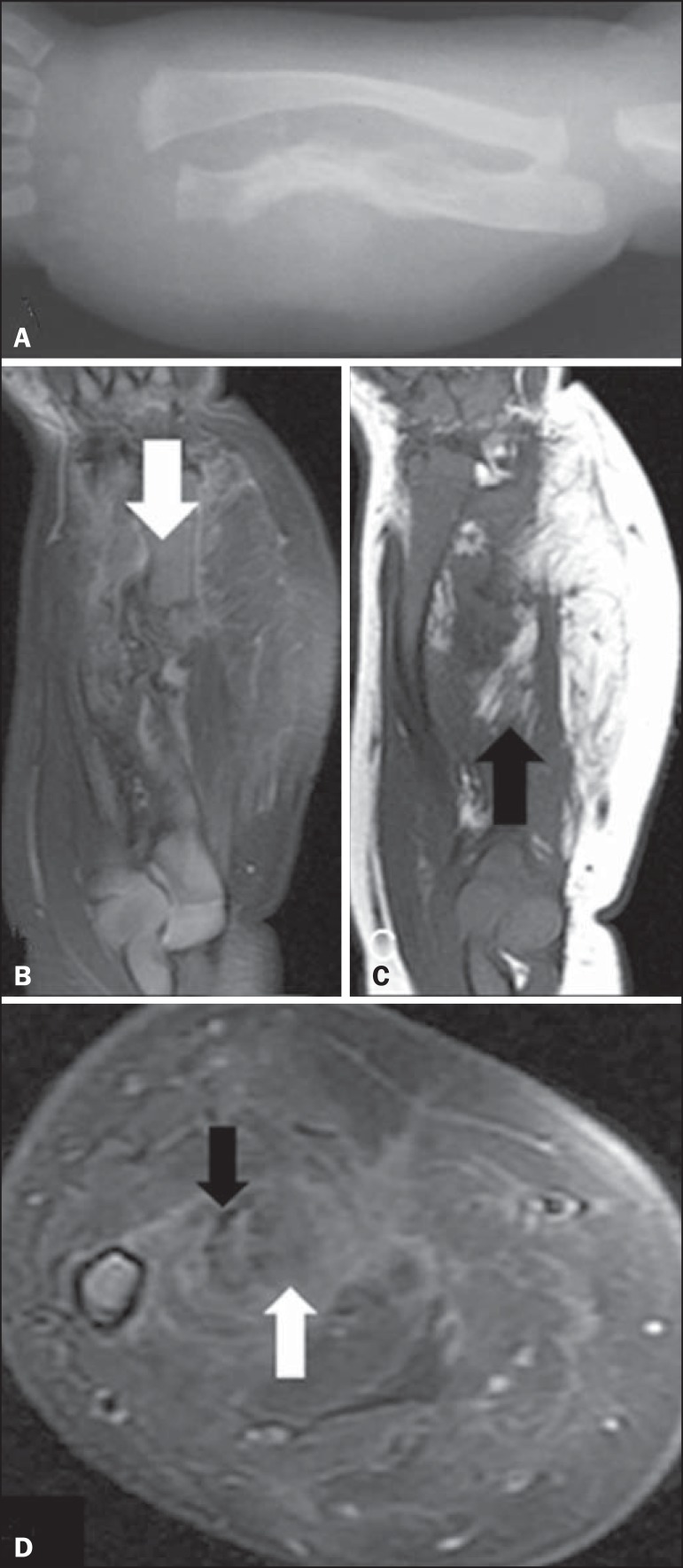
Figure 1.
A: Forearm X-ray showing fracture associated with ulna irregularity and bowing of the radius, together with increased thickness and density of the soft parts of the forearm. B: Fat-saturated, T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan, in the coronal plane, showing discontinuity of the ulna (arrow), the full extent of the lesion, and suppression of the fatty content. C: T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan, in the coronal plane, highlighting the lipid content of the lesion (arrow). D: Proton-density axial magnetic resonance imaging slice in the region of the fractured ulna showing the contrast uptake by the dense fibrous stroma, the fibrotic streaks (black arrow), and the suppressed signaling of the fat content (white arrow).