Figure 1.
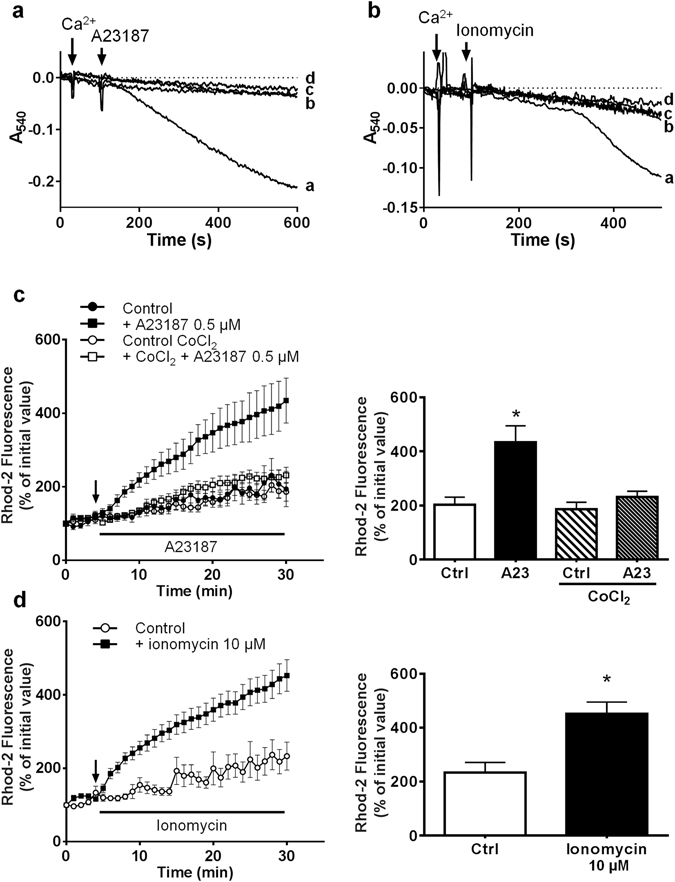
Effect of A23187 and ionomycin on mitochondrial swelling and mitochondrial Ca2+ in isolated cardiomyocytes. (a and b) Swelling was assessed in isolated rat cardiac mitochondria by measuring the change in absorbance of the mitochondrial suspension at 540 nm. Mitochondria were incubated in the presence of rotenone (1 µM) and antimycin A (1 µM) in order to inhibit mitochondrial respiration. Then 200 µM Ca2+ and 1 µM A23187 or 10 µM ionomycin were added. (a) line a: Ca2+ + A23187; line b: Ca2+ + A23187 + CsA 2 µM; line c: Ca2+ alone; line d: A23187 alone. (b) line a: Ca2+ + ionomycin; line b: Ca2+ + ionomycin + CsA 2 µM; line c: Ca2+ alone; line d: ionomycin alone. (c,d) Isolated adult cardiomyocytes were loaded with 5 µM rhod-2 for 40 min at 37 °C and then incubated in a Tyrode’s buffer. After 5 min incubation (arrow) A23187 (c) or ionomycin (d) were added to the medium. Fluorescence values were obtained by averaging pixel intensities after background substraction and were normalised as a percentage of the initial value. Each trace represents the mean ± SEM of 3–5 experiments. *p < 0.05 versus control (Ctrl). The ordinates of the bar graphs are the values of rhod-2 fluorescence observed at 30 min in the corresponding figures.
