Figure 1.
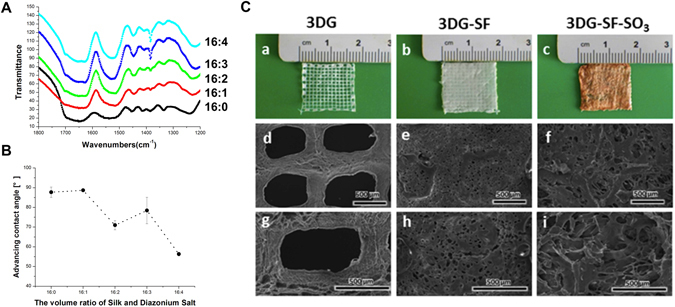
Characterization of scaffolds. (A) Comparison of the ATR-FTIR spectra of unmodified and sulfonated silk. (B) Advancing contact angles of native SF and SF derivatives with 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 volumes per 16 volumes of silk. (C) Micrographs of 3D printed scaffolds (3DG) (a), SF coated 3D printed scaffold (3DG-SF) (b) and SF derivatives coated 3D printed scaffold (3DG-SF-SO3) (c). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of 3DG scaffold (d and g), 3DG-SF scaffold (e and h), and 3DG-SF-SO3 scaffold (f and i), with (g,h,i) at high magnification. The thickness of each layer is 100 μm, and the whole thickness of printed gelatin and gelatin coated with sulfonated silk fibroin scaffold is 1 mm. Scale bars, 500 μm.
