Figure 2.
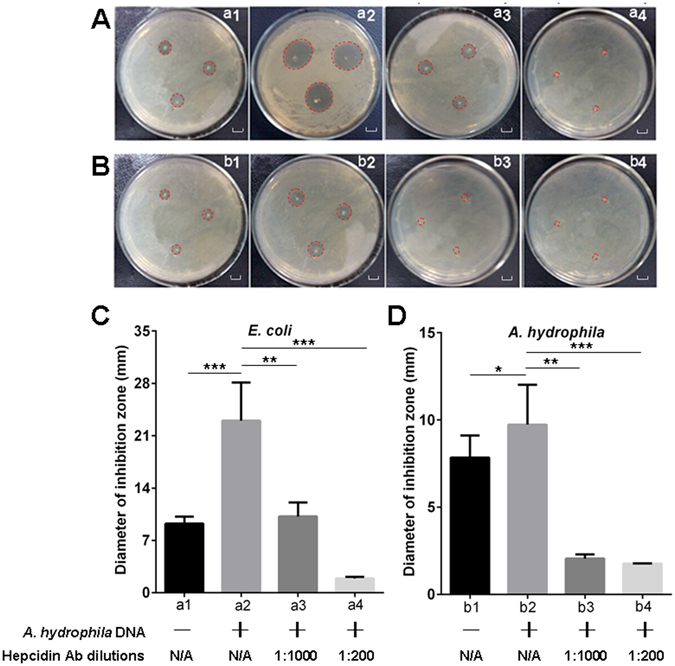
Evaluation of the bactericidal activity of hepcidin in various serum samples against test strains by inhibition zone assay. (A and B) Detection of the inhibition zones for E. coli (A) and A. hydrophila (B) strains by unstimulated serum (a1 and b1), A. hydrophila DNA (1 μg per fish) stimulated serum (a2 and b2), A. hydrophila DNA stimulated serum neutralized with diluted (1:1,000) anti-hepcidin Ab (a3 and b3), and A. hydrophila DNA stimulated serum neutralized with diluted (1:200) anti-hepcidin Ab (a4 and b4), scale bars = 1 cm. (C and D) Measurement of the corresponding diameters of the inhibition zones (mm) from the inhibition zone assays by using serum samples with various treatments against E. coli (C) and A. hydrophila (D) strains. The labels a1 to a4 and b1 to b4 under the horizontal axis of C and D are in accordance with A and B. The annotations “A. hydrophila DNA+/−” and “Hepcidin Ab dilutions” under the labels represent that the E. coli (a1 to a4) and A. hydrophila (b1 to b4) were treated with the serum derived from A. hydrophila DNA stimulated (+) or unstimulated (−) fish, which were in combination with neutralizing the serum with anti-hepcidin Ab at different dilutions (1:1000 and 1:200) or without treatment with the anti-hepcidin Ab (N/A, not applicable). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
