Figure 11.
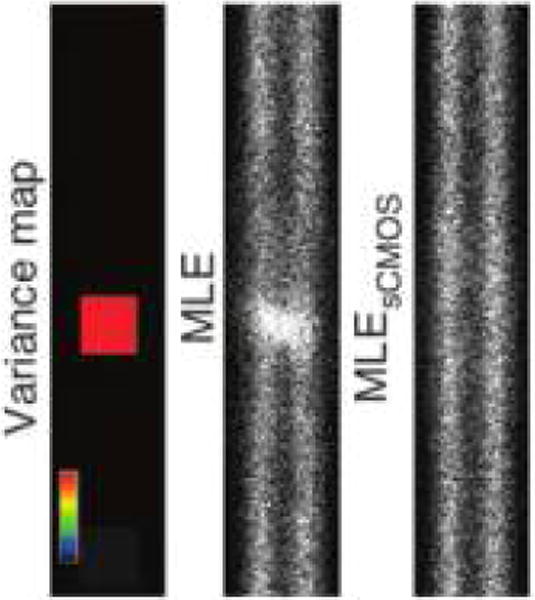
Pixel dependent noise, if known, can be used to refine localization analysis. The left panel displays a simulated “variance map”, where the colorbar indicates the encoding of the noise level, similar to one that could be measured on an sCMOS camera. The color indicates that a single (red) pixel has higher variance, σ, than its neighbors. A MLE for the emitters’ location, shown in the middle panel, that ignores the pixel dependent variance, does not correctly identify the emitter locations that we placed on two parallel lines in this simulation; instead, an artifactual excess of events is detected at the “hot” pixel. On the right panel, we see that the MLE tailored for sCMOS cameras (“MLE-sCMOS”), which does take the variance map into account, avoids this artifact.198 Reproduced with permission from ref 198. Copyright 2013, Nature Publishing Group.
