FIGURE 7.
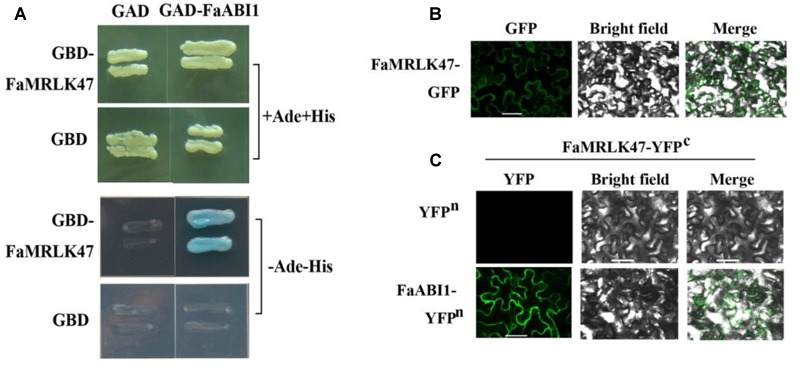
Subcellular localization of FaMRLK47 and physical interaction between FaMRLK47 and FaABI1. (A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of the physical interaction between FaMRLK47 and FaABI1. Protein interactions were examined using combinations of prey and bait vectors. All tests were conducted on media containing adenine (+Ade+His; /–Leu/–Trp/+His/+Ade) or lacking adenine (–Ade–His; /–Leu/–Trp/–His/–Ade). Interactions were determined based on cell growth and were confirmed by an α-Gal assay on medium lacking adenine (/–Leu/–Trp/–His/–Ade). (B) Subcellular localization of FaMRLK47. pMDC83-FaMRLK47 was transformed into tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cells, and fluorescence was observed by confocal microscopy as described in Section “Materials and Methods.” Bars = 50 μm. (C) BiFC analysis of the physical interaction between FaMRLK47 and FaABI1. FaMRLK47 and FaABI1 were fused with the C and N terminus of yellow fluorescent protein (YFP; designated as YFPc and YFPn, respectively). Different combinations of the fused constructs were co-transformed into tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cells, and the cells were visualized using confocal microscopy as described in Section “Materials and Methods.” YFP and bright field were excited at 488 and 543 nm, respectively. Bars = 50 μm.
