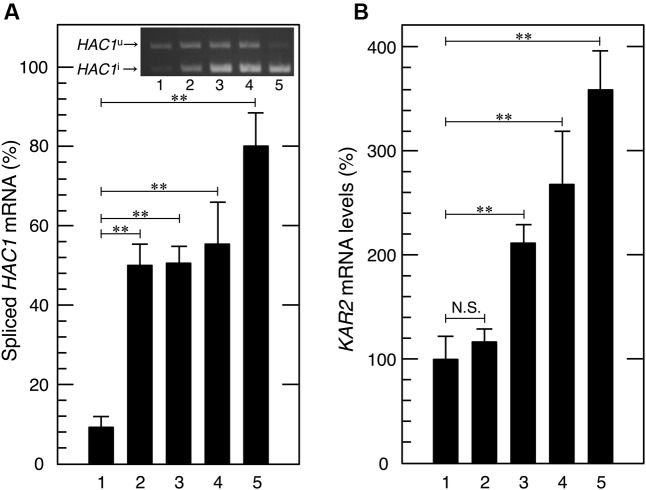
FIGURE 3.
Acetic acid induced the splicing of HAC1 mRNA and transcriptional activation of KAR2, a target gene of Hac1p. Exponentially growing cells were exposed to the indicated stress conditions. (A) Total RNA samples from cells treated with acetic acid or DTT were subjected to RT-PCR in order to amplify the HAC1 products. HAC1u and HAC1i were fractionated using 2.0% agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, w/o stress; lane 2, 0.3% acetic acid for 15 min, lane 3, 0.3% acetic acid for 30 min; lane 4, 0.3% acetic acid for 60 min; lane 5, 10 mM DTT for 60 min. (B) KAR2 mRNA levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR. In order to compare expression levels, the mRNA level of KAR2 was normalized to that of ACT1 under each condition. The mRNA level in cells without a stress treatment was considered to be 100%. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error (n = 3). Lane 1, w/o stress; lane 2, 0.1% acetic acid for 60 min, lane 3, 0.2% acetic acid for 60 min; lane 4, 0.3% acetic acid for 60 min; lane 5, 10 mM DTT for 60 min. ∗∗P-value < 0.01. N.S., no statistically significant difference.