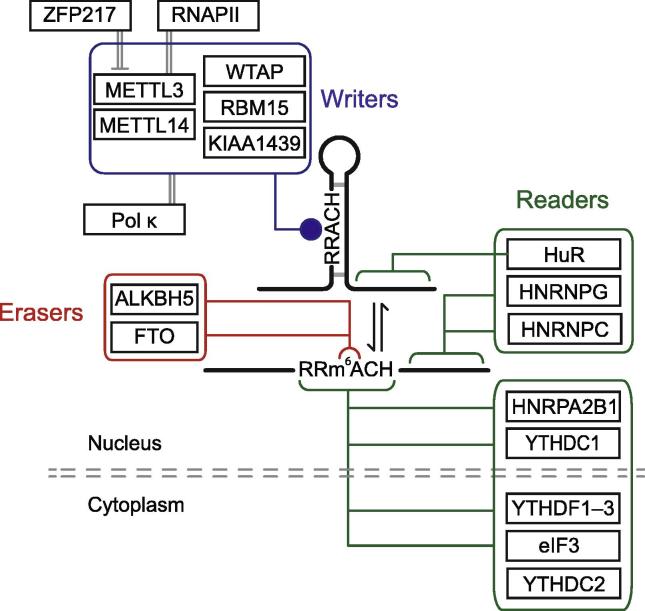
Figure 1.
The m6A regulatory pathway
Schematic representation of known components of the m6A regulatory pathways. The methylase complex (contained in the blue box) can modify adenosines in an RRACH context (R = G/A, H = G/A/C). The function of the methylase complex can be inhibited by ZNF217. The methylase complex interacts with RNAPII during transcription and recruits Pol κ to sites of DNA damage. Deposition of m6A can alter the RNA secondary structure. The demethylases (contained in the red box) can remove the methyl group. Two types of reader proteins (included in the green boxes) can interact with modified RNA through direct recognition of the methyl group or interaction with an RNA secondary structure induced by m6A modification. ALKBH5, alkB homolog 5; eIF3, eukaryotic initiation factor 3; FTO, fat mass and obesity-associated protein; HNRNPA2B1, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1; HuR, human antigen R; METTL3, methyltransferase like 3; Pol κ, DNA polymerase κ; PBM15, RNA binding motif protein 15; RNAPII, RNA polymerase II; WTAP, WT1-associated protein; YTHDC1, YTH domain containing 1; YTHDF, YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein; ZFP217, zinc finger protein 217.