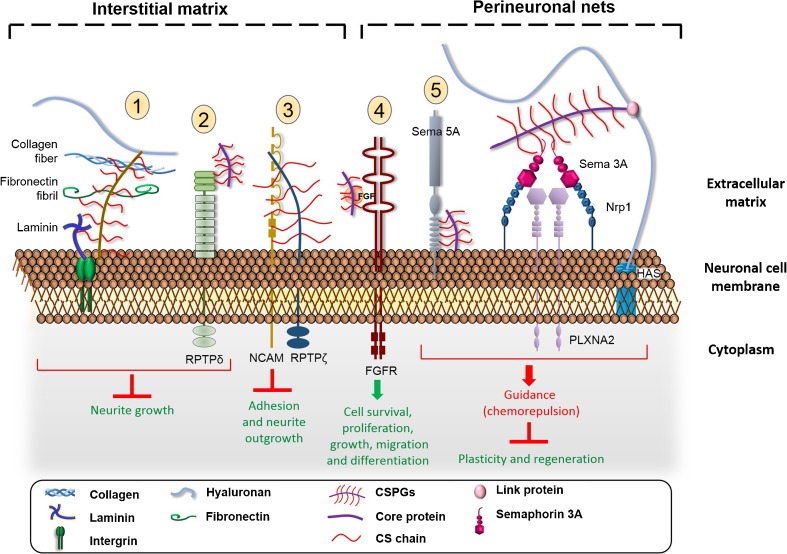
Fig. 3.
Interaction of CS glycan chains with different protein families in CNS matrix. CSPGs inhibit the growth cone via the interaction of its CS chain with 1) laminin and collagen and 2) bind its receptor protein tyrosine kinase (RPTP). 3) The neuronal adhesion molecule NCAM interacts with phosphacan (the extracellular part of RPTPζ) by its CS chain and results in an inhibition of adhesion and neurite growth. 4) CS, notably CS-E, acts as a binding partner of FGF to promote growth and differentiation. 5) An interaction of semaphorin 5 A (Sema 5A) with CS chain turns the attractive guidance protein into a repulsive cue. Semaphorin 3A (Sema 3A) is a repulsive guidance protein found in perineuronal nets and interacts specifically with CS-E motif. It exerts its chemorepulsive effect by signalling via plexin-neuropilin receptors. CS could be an additional constituent of sema 3A signalling complex