Fig. 1.
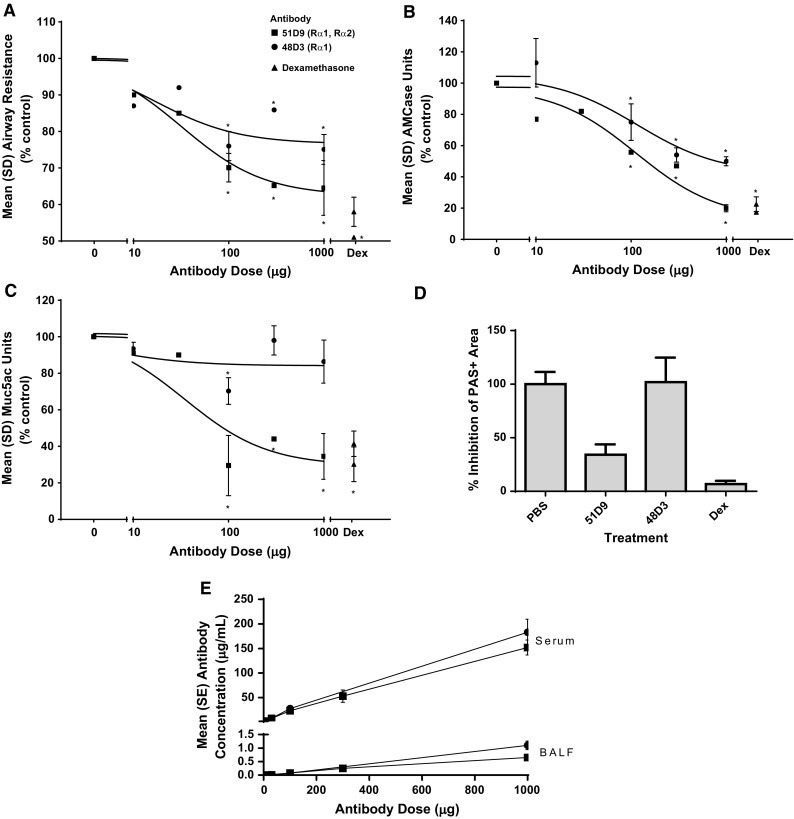
Anti-IL-13 antibody effects in the murine OVA-induced asthma model. Measurement of a AHR, b AMCase levels in the BALF, and c, d mucus production measured by Muc5ac ELISA and histologic assessment by PAS reactivity following administration of antibody 51D9 or 48D3 before OVA challenge. a–c Anti-mIL-13 antibodies that block binding of IL-13 to either IL-13Rα1 alone or both IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2 similarly inhibit AHR and AMCase production, whereas blockade of IL-13Rα2 binding appears to be required for inhibition of mucus production. Pooled data from 3–4 studies; n = 10–30/data point. d Area of mucus-secreting epithelial cells visualized by PAS+ staining in OVA-challenged animals treated with either 51D9, 48D3, or dexamethasome. e Quantification of antibody levels in both serum and BALF of treated mice measured at the termination of the experiment. AHR airway hyperresponsiveness, AMCase acidic mammalian chitinase, ANOVA analysis of variance, BALF bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, Dex dexamethasone, ELISA enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, IL interleukin, mIL-13 mouse IL-13, Muc5ac mucin 5ac, OVA ovalbumin, PAS periodic acid-Schiff, PBS phosphate-buffered saline, R receptor. *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA and the Dunnett posttest
