Figure 1.
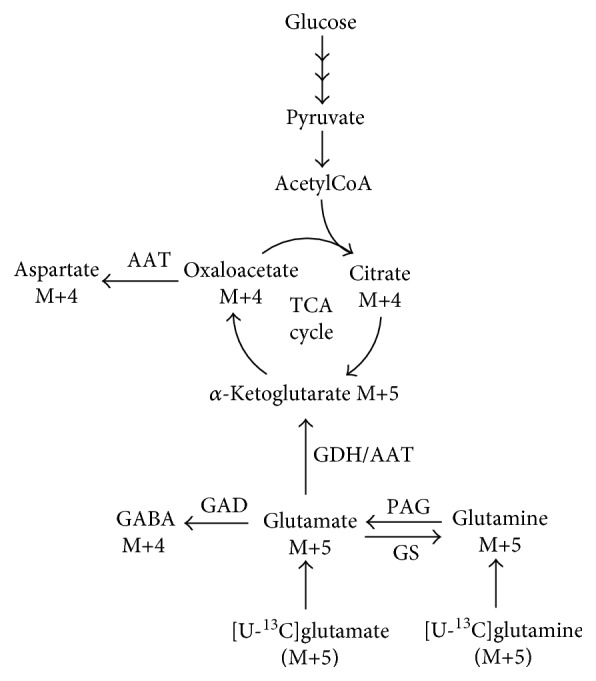
Cartoon illustrating 13C labeling patterns from [U-13C]glutamate and [U-13C]glutamine metabolism. Glutamate M+5 can be converted into glutamine M+5 or GABA M+4 through glutamine synthetase (GS) or glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) activity, respectively. Glutamine M+5 can likewise be converted into glutamate M+5 through the action of phosphate-activated glutaminase (PAG). Additionally, glutamate M+5 can be converted into α-ketoglutarate M+5 by activity of either glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) or aspartate aminotransferase (AAT) and be introduced into the TCA cycle. α-Ketoglutarate M+5 can be metabolized in the TCA cycle, giving rise to 13C labeling in all TCA cycle intermediates. Aspartate is in close equilibrium with oxaloacetate trough AAT, giving rise to aspartate M+4 labeling.
