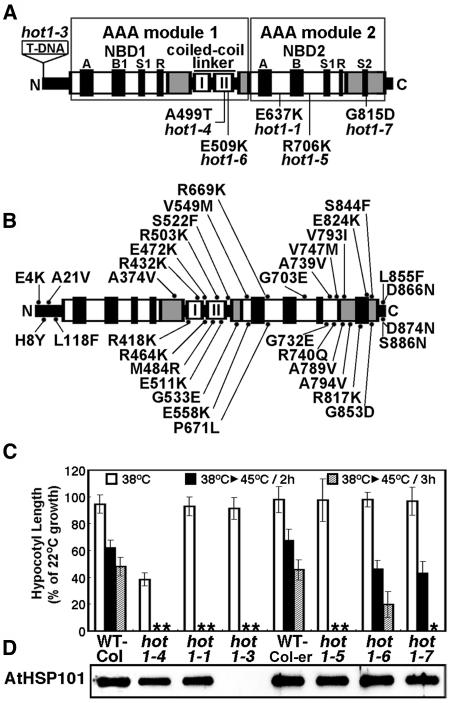
Figure 1.
Location and Phenotype of Mutations in AtHsp101 (See Also Supplemental Figure 1 Online).
(A) Location of hot1 mutations with a thermotolerance phenotype on a schematic diagram of the AtHsp101 protein. The conserved AAA modules consist of two domains, a nucleotide binding domain (NBD1 or 2), containing conserved motifs [Walker A, Walker B, Sensor 1(S1), and Arg finger (R)], and a C-terminal small domain (gray boxes), containing Sensor 2 (S2) in AAA2. The coiled-coil domain contains two signature motifs (Lee et al., 2003), with hot1-4 located in signature motif II.
(B) Location of missense mutations that are wild type for thermotolerance, which were obtained by Tilling analysis (see Methods).
(C) Quantitative assessment of thermotolerance in hot1 mutant seedlings compared with their corresponding wild type (Columbia for hot1-1 and hot1-4, Columbia erecta for all others). After growth for 2.5 d in the dark at 22°C, seedlings were pretreated at 38°C for 90 min and returned to 22°C for 2.5 d (38°C samples), or pretreatment was followed by 2 h at 22°C then 2 or 3 h at 45°C before 2.5 d of recovery (38°C > 45°C samples). hot1-4 seedlings are more sensitive to 38°C treatment than wild-type or null alleles. Asterisks indicate values equal to zero. Mean and standard deviations were derived by measurement from three independent experiments performed with 60 or more seedlings per mutant and values plotted as a percentage of the 22°C value.
(D) Protein gel blot analysis of AtHsp101 protein levels in wild-type and hot1 seedlings after treatment at 38°C.