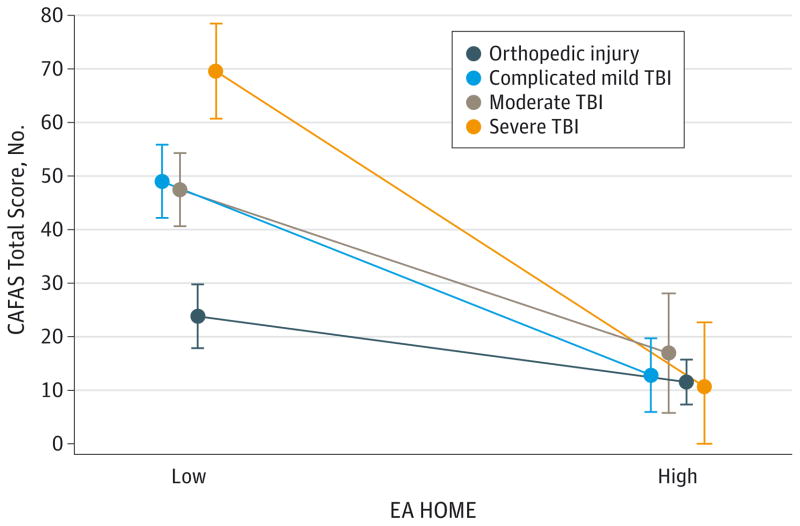
Figure 3. Adjusted Mean Levels by Group at Low/High Levels of Facilitative Home Environments.
Significant group by home environment interaction (F3,114 = 3.28; P = .02) revealed significantly poorer long-term functioning outcomes for children with a traumatic brain injury (TBI) than children with an orthopedic injury when the home environment had low enrichment, while high facilitative home environments revealed no significant group differences in functional impairment. EA HOME indicates the early adolescent version of the Home Observation for Measures of the Environment. Error bars indicate ±1 SE.