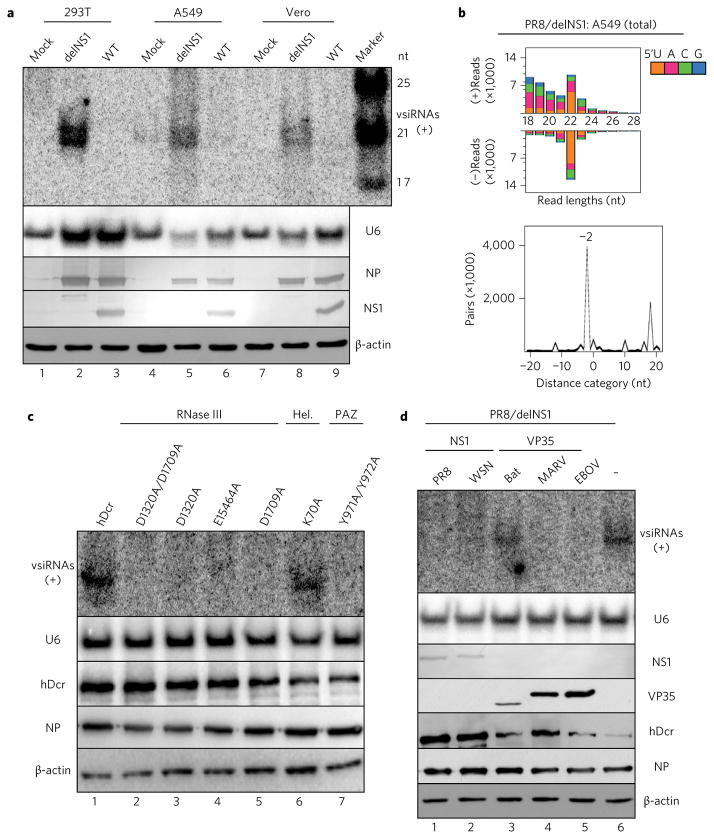
Figure 3. Induction and suppression of influenza vsiRNA biogenesis in distinct human and monkey somatic cells.
a, Northern detection of the influenza vsiRNAs in human (293T and A549) and monkey (Vero) cells 24 h after infection with WT or mutant (delNS1) viruses of the PR8 strain. b, Properties of influenza vsiRNAs (per million total mature miRNAs) sequenced directly without AGO co-IP from PR8/delNS1-infected A549 cells. c, Production of influenza vsiRNAs in PR8/delNS1-infected hDcr-KO 293T cells ectopically expressing WT hDcr, or hDcr mutants carrying the point amino acid mutations29 known to disrupt the function of the helicase (Hel.; K70A), PAZ (Y971A and Y972A), RNase IIIA (D1320A and E1564A) or RNase IIIB (D1709A) domain of hDcr. d, Suppression of influenza vsiRNA biogenesis in PR8/delNS1-infected hDcr-KO 293T cells ectopically expressing hDcr by NS1 of IAV strain PR8 or WSN, FLAG-tagged VP35 of Ebola virus (EBOV), Marburg virus (MARV) or bat, as indicated. The same sets of RNA and protein samples were used for northern or western blot detection of the positive (+)-strand influenza vsiRNAs, U6 RNA, viral NP and NS1 proteins, FLAG-tagged VP35 variants, hDcr or β-actin as in Fig. 2. Each experiment was repeated twice, with reproducible results.