Fig. 8.
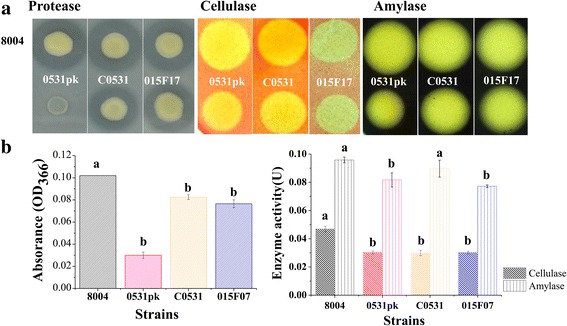
Examination of extracellular enzymes’ activities. a Overnight culture (3 ul) was spotted onto NYGA plates containing 1% skim milk (for protease), after incubation at 28 °C for 24 h, plates were photographed. For cellulose, 3 ul overnight culture was spotted onto NYGA plates containing 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose after incubation at 28 °C for 48 h, plates were stained by I2/KI (0.08 M I2, 3.2 M KI) and washed by 70% ethyl alcohol. For amylse, 3 ul overnight cultures were spotted onto NYGA plates containing 0.1% starch incubation at 28 °C for 24 h. The plates were stained by 0.1% Congo Red and then washed 2 times. At last plates were destained by 1 M NaCl solution. b For extracellular protease activity, the method described by Swift and associates was used. 10 μl of enzyme-containing extracts were added to 200 μl of indicator buffer containing 1% (wt/vol) carboxymethyl cellulose as the substrate. The reactions were carried out for 30 min at 28 °C. The released reducing sugars were measured as D-glucose equivalents, as described by Miller. One unit (U) of the cellulase (endoglucanase) activity was defined as the amount of enzyme releasing 1 μmol of reducing sugar per minute. Amylase activity quantification was conducted in the same way as for the cellulose (endoglucanase) measurement, except that the substrate 1% (wt/vol) CMC was replaced by 1% (wt/vol) starch solution. Different letters within one enzyme activity assay indicate significant differences at a level of α < 0.05 based on Duncan’s test by one way-ANOVA
