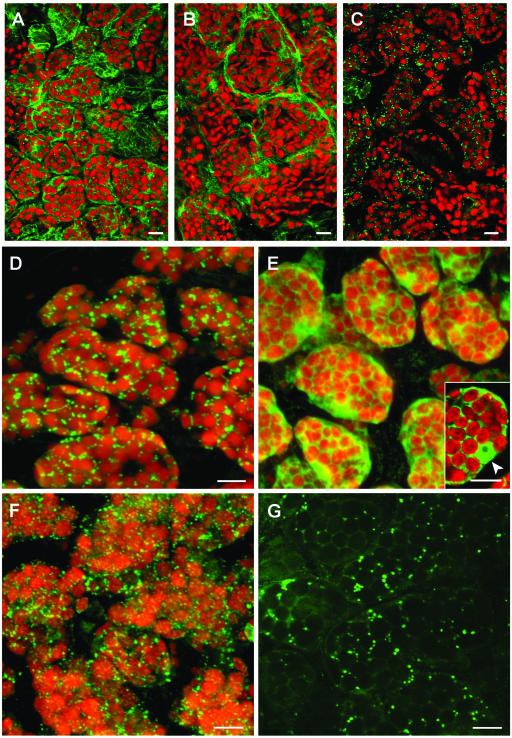
Figure 3.
Whole-mount immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of 6-d-old Arabidopsis cotyledons. A to D, Double-fluorescence x-y confocal optical sections of wild-type Arabidopsis cotyledon parenchyma cells showing endogenous plastid fluorescence (red) and subcellular immunodetection (green) of α-TIP (A), FPS1 (B), and HMGR1 (anti-CD1 antibodies; C and D). E and F, Double-fluorescence confocal imaging of the autofluorescence of plastids (red) and anti-CD1 antibodies (green) in cotyledons of plants stably transformed with the catalytic domain of HMGR1 (CD1; E), and with isoform HMGR1S (F). Inset in E is a representative middle section showing the cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of the catalytic domain of HMGR1. The nucleus, containing a nucleolus, is indicated with an arrowhead. G, Single confocal section in a nontransformed cotyledon cell imaged with increased photomultiplier intensity of the green channel revealing HMGR signal in spherical structures as well as in a polygonal, reticular network. A to F, Three-dimensional projections of a series of 40 to 50 sections with a z step of 0.25 μm. Scale bars = 100 μm (A–C); 10 μm (D–G).