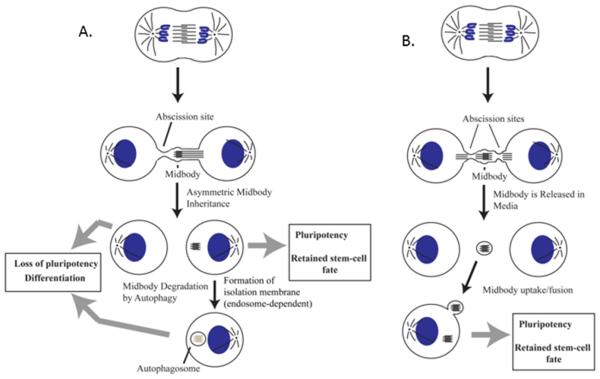
Figure 1. Midbodies can either be asymmetrically inherited or released into the extracellular space.
(A) Model detailing the possible fates of an asymmetrically inherited midbody. Upon asymmetric inheritance, the midbody can remain as a post-mitotic midbody in the cell and potentially influence pluripotency, or can be degraded via autophagy.
(B) Model detailing the possible fate of a midbody following symmetric division, where it is released into extracellular space and can be potentially uptaken by surrounding cells.