Figure 4.
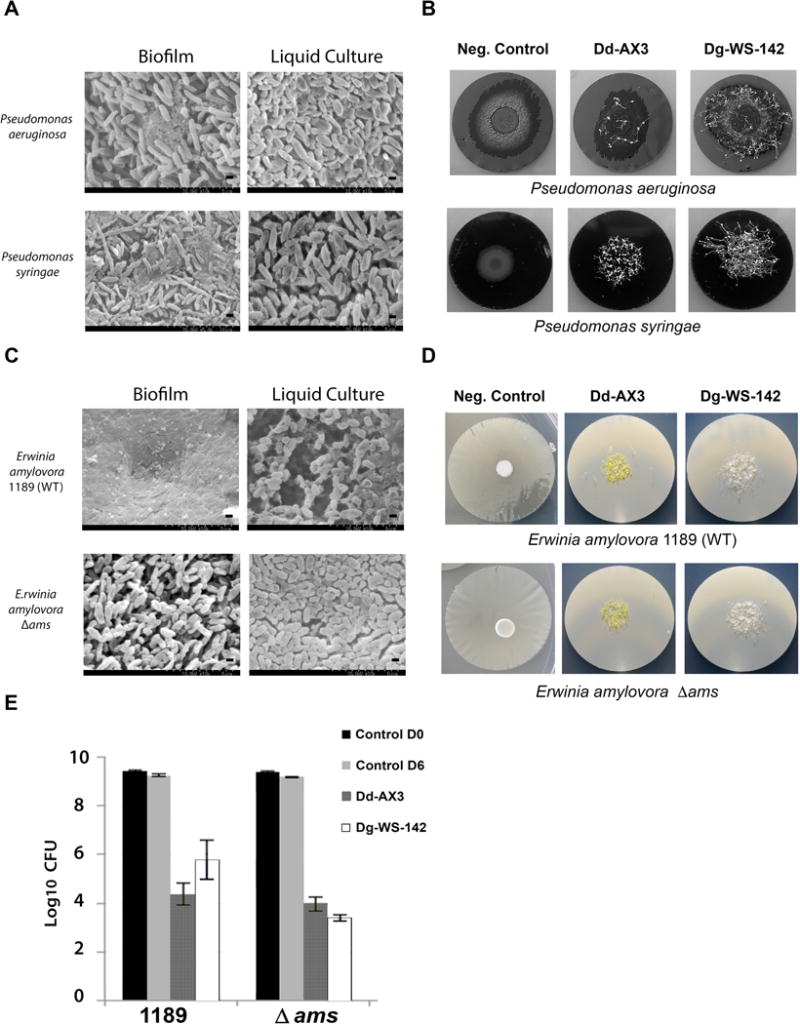
Anti-biofilm activities of dictyostelid myxamoebae against other Gram negative bacterial pathogens of plants and animals. (A) SEM images showing composition differences of” Biofilm” and planktonic (“Liquid Culture”) specimens of P. aeruginosa and P. syringae. Scale bars are provided (2.5μm and 5 μm). (B) Images of P. aeruginosa and P. syringae biofilms grown on PC membranes 7 days after inoculation with 2.5 × 104 dictyostelid spores. Negative Control biofilms were not inoculated with dictyostelids. Images show biofilm destruction and the formation of multicellular fruiting bodies (fluffy patches). (C) SEM images of E. amylovora 1189 and E. amylovora 1189 Δ ams “Biofilm” and planktonic “Liquid Culture” specimens. (D) Corresponding macroscale images of E. amylovora 1189 and E. amylovora 1189 Δ ams on PC membranes 5 days after inoculation with 2.5 × 104 spores of Dd-AX3 or Dg-WS-142. (E) Quantification of surviving bacteria after 5 days’ treatment with 2.5 × 104 spores (inoculum size) of Dd-AX3 or Dg-WS-142. Averages of two experiments, each experiment was performed with duplicate PC filters.
